glibc中的bins链表详解
glibc中的bins链表详解
[toc]
不知道是否有师傅和我一样,有时候会迷失在glibc的链表中,傻傻分不清楚fd和bk指向的是什么,也会忘记chunk的释放和分配顺序。因此就有了这篇文章,以一系列小实验来记录下各个链表的fd、bk指针的作用,以及各个链表的分配顺序。
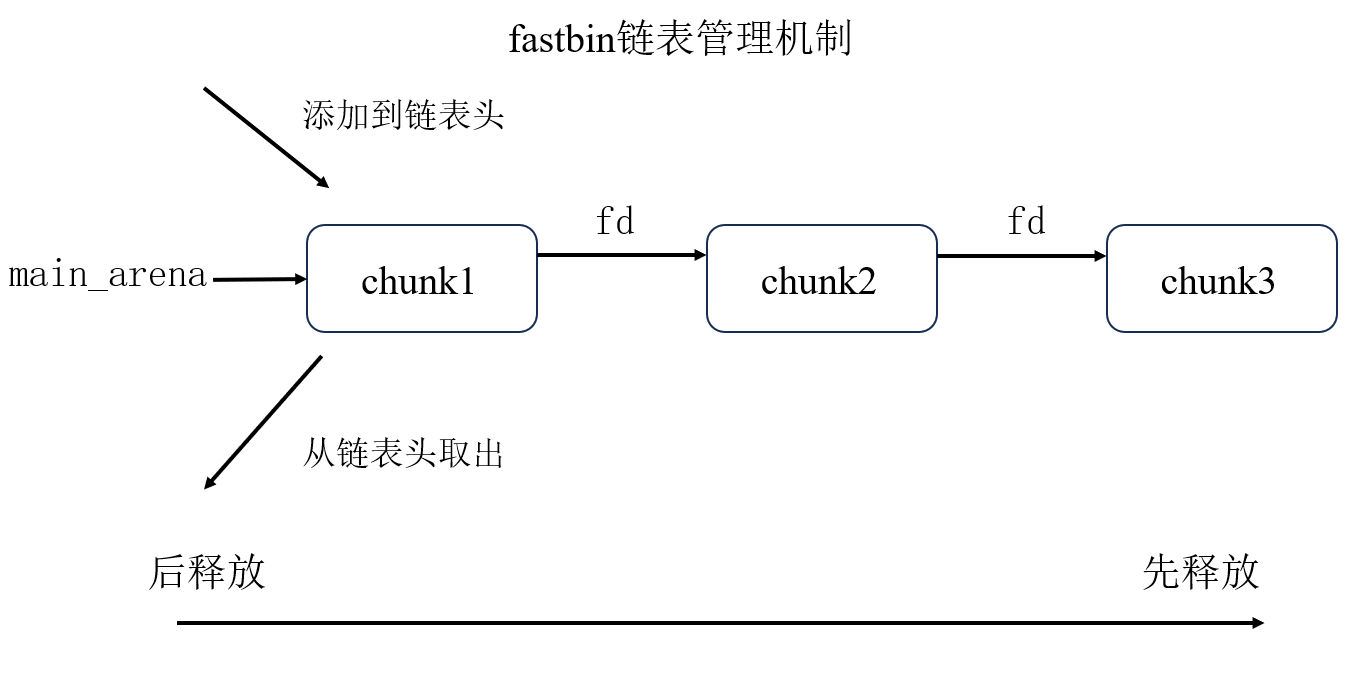
fastbin
通过以下代码在glibc2.23进行测试:
1 | |
其输出为:
1 | |
这证明:
fastbin是LIFO(Last in, Fist out),即最后释放的chunk会最先被申请回去。这种分配方式满足操作系统上的时间局部性。fastbin中只存在fd指针,不存在bk指针,后释放的chunk的fd指针指向先释放的chunk。- 从链表头添加,从链表头取出。
即:
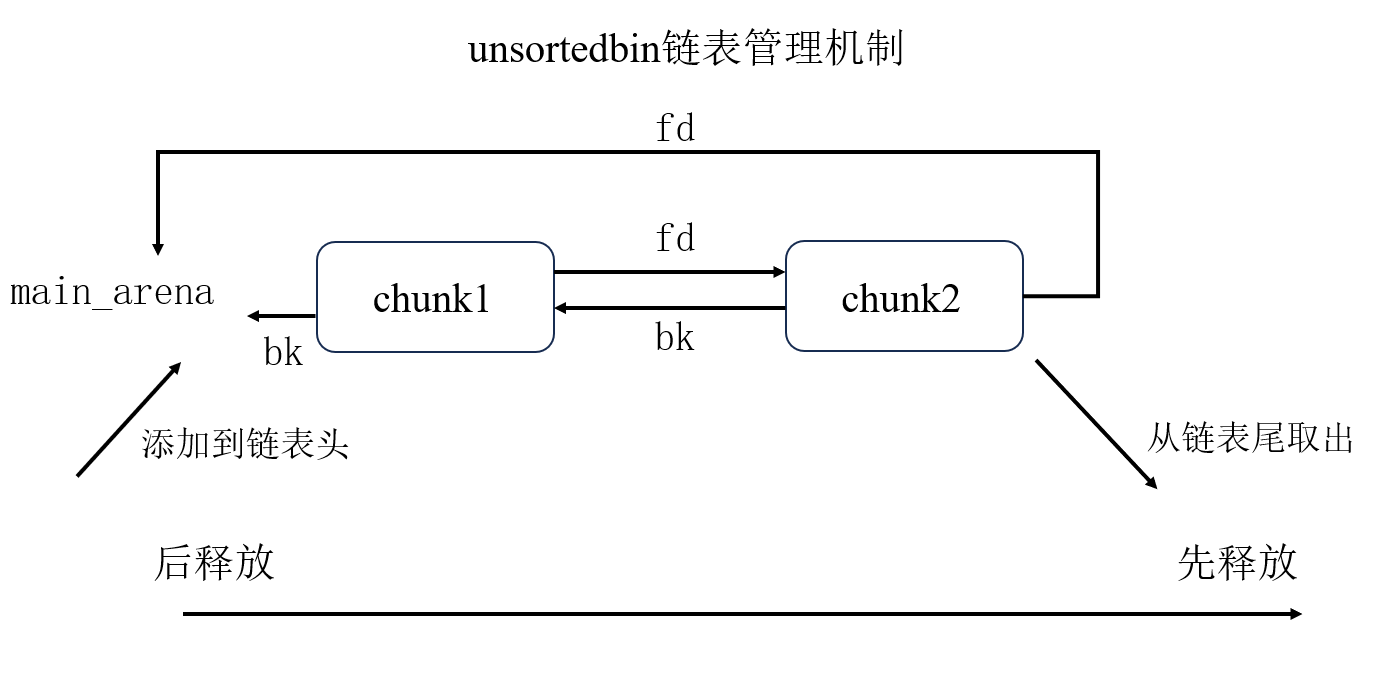
unsortedbin
通过以下代码在glibc2.23进行测试:
1 | |
其输出为:
1 | |
这说明:
unsortedbin是遵循FIFO(First in, First out)的,即先释放的会先被申请出去。unsortedbin的fd指针指向比他先释放的chunk,而bk指针指向比它后释放的chunk。fd和bk指针都会指向main_arena,因此最先释放的chunk的fd指针将会指向main_arena,而最后释放的chunk的bk指针会指向main_arena。- 从链表头插入,从链表尾取出
即:
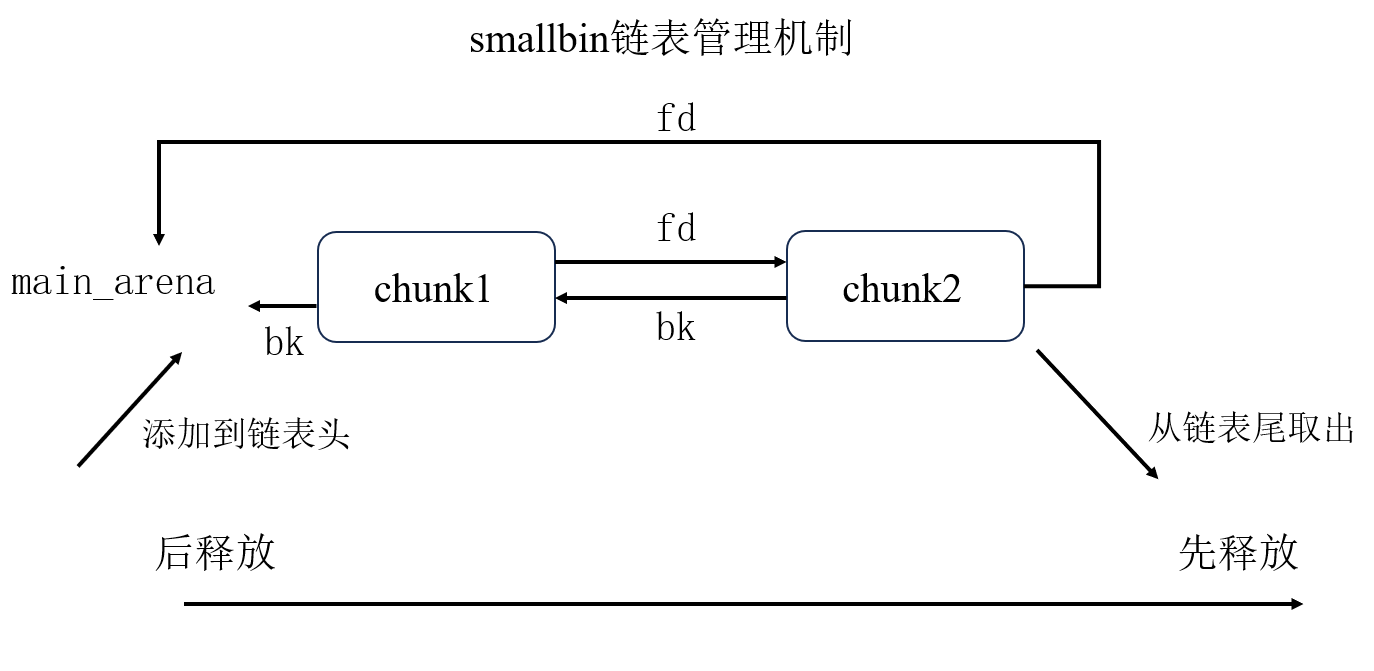
smallbin
通过以下代码在glibc2.23进行测试:
1 | |
其输出为:
1 | |
这说明:
- 其和
unsortedbin的管理机制基本一样,同样为FIFO,只是unsortedbin只有一条链,而smallbin根据大小不同,有很多链。 smallbin的fd指针指向比他先释放的chunk,而bk指针指向比它后释放的chunk。fd和bk指针都会指向main_arena,因此最先释放的chunk的fd指针将会指向main_arena,而最后释放的chunk的bk指针会指向main_arena。- 从链表头插入,从链表尾取出
即:
largebin
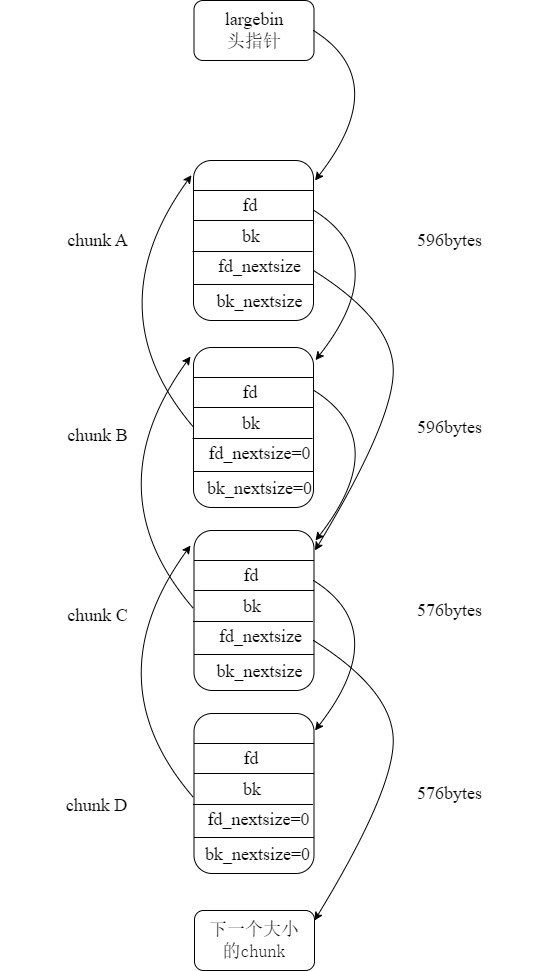
largebin的链表结构比较复杂,若仍然使用代码的形式给读者展示,比较晦涩。这部分内容可以查看Rolan师傅的文章进行参考。这里放一张以前画的largebin的结构图。
其中:
每一个
largebin中存放的chunk大小是不相同的,一共有63个largebin。在这63个largebin中,前32个largebin的最大chunk和最小的chunk之差为64bytes(0x40)。例如第一个largebin的大小为512bytes-568bytes(32位),而第二个largebin的大小就为576bytes-632bytes。每一个
largebin中的chunk按照大小顺序从大到小排序。若大小相同,则会按照释放顺序排序:最先释放的
chunk拥有fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize指针,之后的chunk的这两个指针的值都为0。若将这个chunk称为小堆头,那么后面释放的chunk都会被插入到小堆头的后面。因此,对于同一个大小的large chunk,最先释放的在最上面,除此之外越先释放在越后面。fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize是指向当前bin的下一个大小的chunk。fd_nextsize指向比自己小的,而bk_nextsize指向比自己大的。
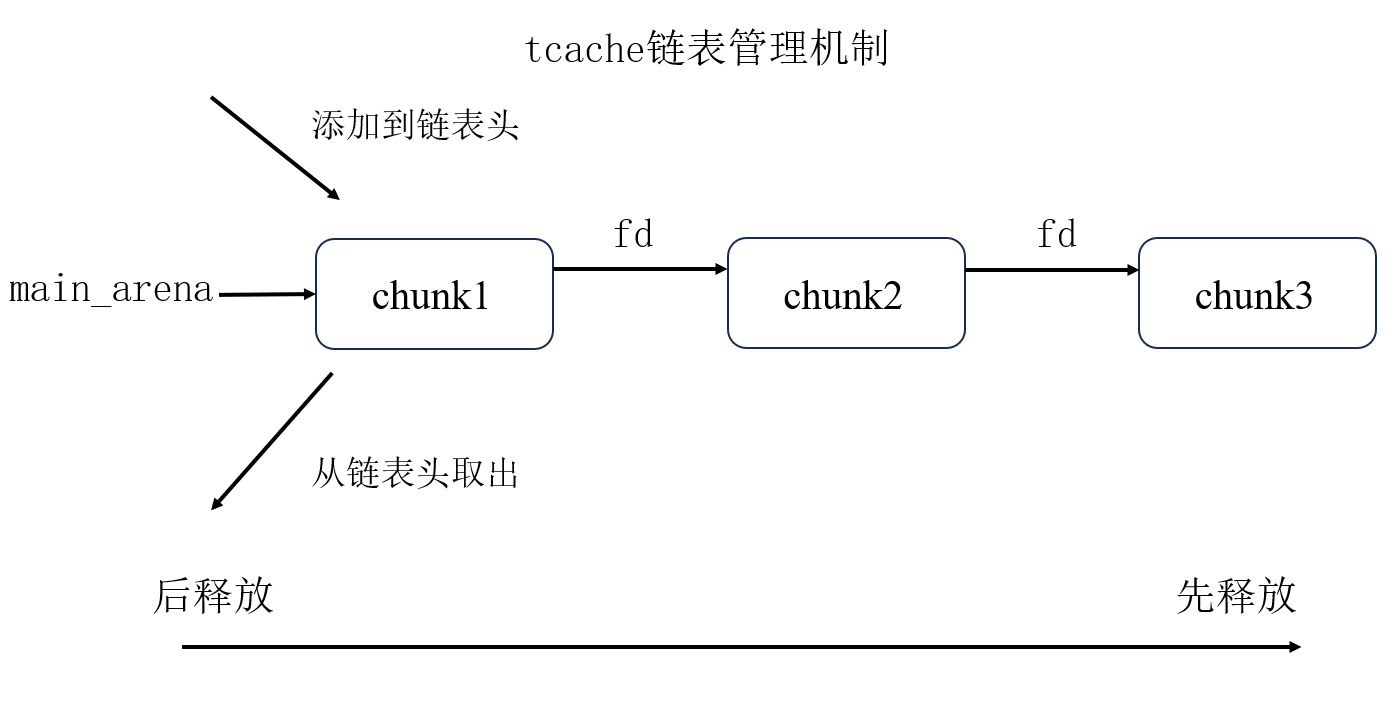
tcache
通过以下代码在glibc2.27下完成测试:
1 | |
其结果如下:
(根据glibc版本的不同,其bk指针有差异,指示的是其安全规则)
1 | |
从上面可以看到:
tcache的管理机制和fastbin的管理机制很像,区别在于tcache还包括smallbin大小,且其bk指针用于安全校验。tcache是LIFO(Last in, Fist out),即最后释放的chunk会最先被申请回去。这种分配方式满足操作系统上的时间局部性。tcache同样也是后释放的chunk的fd指针指向先释放的chunk。- 从链表头添加,从链表头取出。
即:(是的,我只需要更改fastbin为tcache即可。)